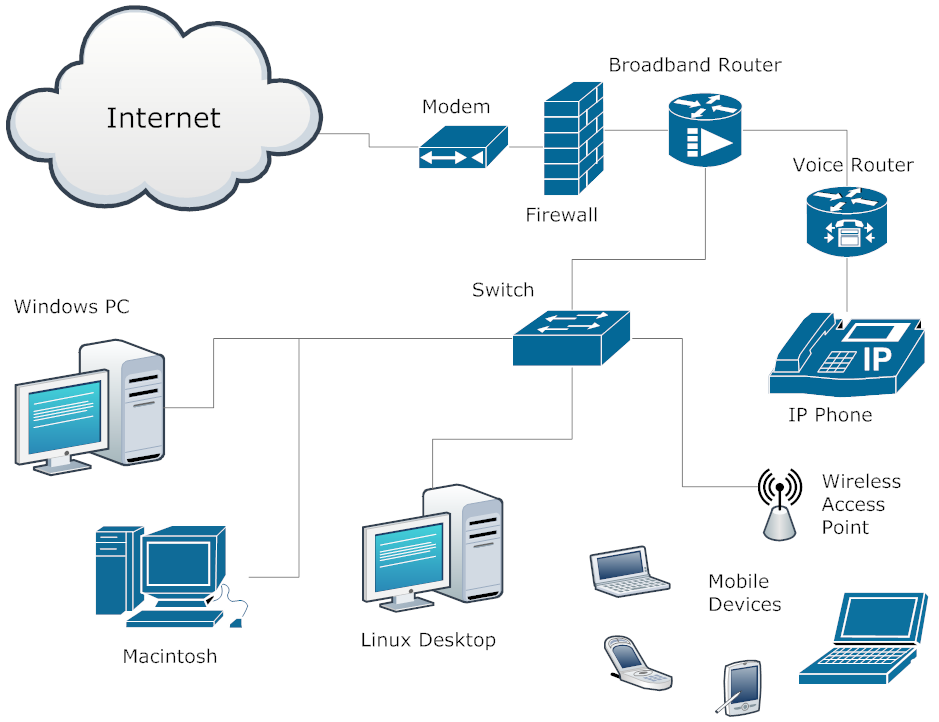
Things to Avoid in Running Network Cabling
 What can cabling that has not been installed properly do?
What can cabling that has not been installed properly do?
It can lead to a lot of negative outcomes such as paralyzed network performance, maintenance troubles and hidden costs. Network cabling can be especially troublesome if it is installed by individuals without the proper knowledge and tools. When it comes to twisted pair cabling, there are many factors that you need to consider.
In the past, many companies installed different cable systems since twisted pair cabling was expensive. At present, full installation is still costly although a greater part of the expense is labor since raw cables is not pricey. Cable management is another concern. Use of ladder racks means additional cost but it reduces upkeep. Also be sure you label cables and to make use of color codes.
Unshielded twisted pairs are more practical in terms of usage. Magnetic fields are produced by low voltages that pass through your cables. This is a vital property of the communications cycle. And if you run unshielded cables along with electrical wires, the magnetic field can be interrupted. The communications becomes corrupted or noisy. You can expect that transmissions will not make it from one point to the other. Another possibility is that transmission rates will become slower. The cables should be perpendicular with electrical lines instead with the electric wires inside of shielded tubes at cross points.
Do not attempt to run cable alongside fixtures that create “noise”. Fluorescent lamps, motors and devices that generate electrical or magnetic interference will distort your cabling infrastructure. Install a data cable conduit that will create a buffer from these hazards. Also figure out the total distance of each cable. This is usually up to 100 meters. However, if cabling data rates reaches 10 to 40 GBPs, be attentive about distance restrictions related to the kind of cabling you plan to use. If you will run 10 GBPs for a maximum of 100 meters over twisted pair cabling, it is best to use Category 6 cabling.
Be aware of local codes.
This is important for safety concerns. In many areas, using PVC-covered cables is not allowed in air-handling spaces. When PVC burns, there is toxic emission that may prove dangerous to firefighters and other safety personnel who will try to navigate the location during emergencies. Failure to follow rules can lead to fines and forced replacement of cabling infrastructure. Contractors must be mindful of these regulatory standards.


 t connects personal computers to the wall plate or provides the short interconnects among the switches, routers and the patch panels in the wall closet or Server Room. These make use of stranded wires instead of solid to increase flexibility. It also lessens the risk of cracking when you unplug the cable. There is also a variety of Ethernet patch called the crossover cable. It is used to hook up two PCs together and sometimes to interconnect switches.
t connects personal computers to the wall plate or provides the short interconnects among the switches, routers and the patch panels in the wall closet or Server Room. These make use of stranded wires instead of solid to increase flexibility. It also lessens the risk of cracking when you unplug the cable. There is also a variety of Ethernet patch called the crossover cable. It is used to hook up two PCs together and sometimes to interconnect switches.


 Riser cables were designed for non-plenum vertical applications like between the floors of multi-story buildings. They are also described as backbone cables. These
Riser cables were designed for non-plenum vertical applications like between the floors of multi-story buildings. They are also described as backbone cables. These 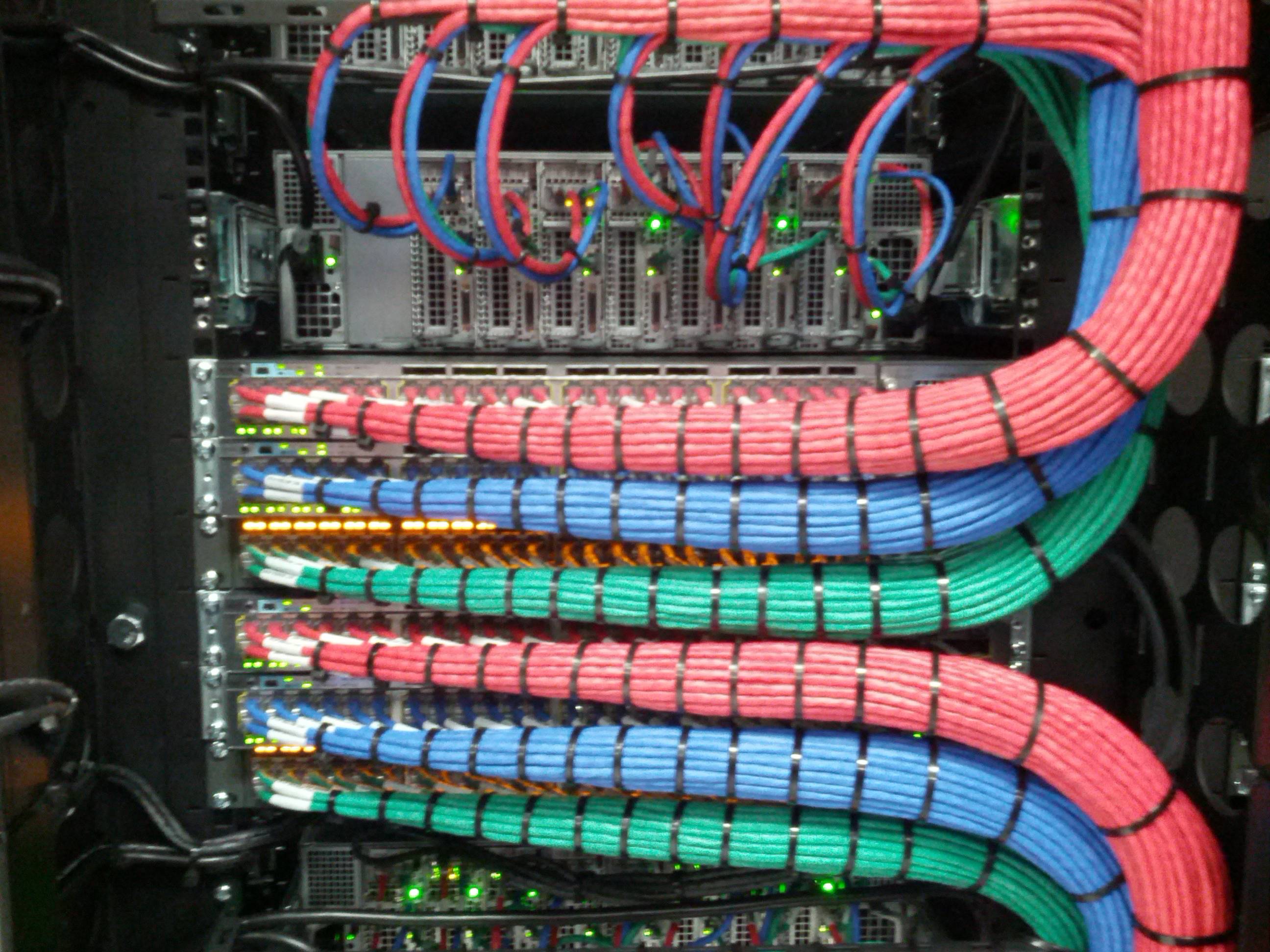
 It can lead to a lot of negative outcomes such as paralyzed
It can lead to a lot of negative outcomes such as paralyzed 
 Networking cabling is not a simple task. It entails expertise and attention to detail. What are valuable insights that
Networking cabling is not a simple task. It entails expertise and attention to detail. What are valuable insights that 
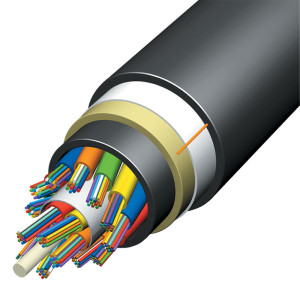 Optical fiber
Optical fiber 
 The
The