
Planning – Network Design Requirements
 After receiving the requirements for a network, it is common for designers to prioritize their implementation and integrate them into the format of the design. Occasionally, they initially rely on best practices, instead of focusing on planning. This is unfortunate because the planning process often leads to discovering multiple viable design solutions.
After receiving the requirements for a network, it is common for designers to prioritize their implementation and integrate them into the format of the design. Occasionally, they initially rely on best practices, instead of focusing on planning. This is unfortunate because the planning process often leads to discovering multiple viable design solutions.
Designers should first make business-centric decisions determining either the solution or design that supports the company’s objectives or strategy. Although it is advisable to follow best practices for network design, reliance on them is more typical on occasions when a network is being designed from the ground up, which is usually not the case for large service providers and enterprises.
Let’s consider optimizing office buildings as a comparison. The standard procedure for civil engineers and architects is to perform an evaluation of a building by identifying existing problems, understanding the organization’s goals, and gathering business requirements. Afterwards, they begin optimizing the office building’s existing features. As examples, this may involve replacing the elevators or expanding the lobby.
The above is similar to the procedure for revamping network design. There will always be faulty designs that were poorly planned. Sometimes they are unable to scale, or adopt emerging technologies, or adapt to changing business conditions. Thus, designers must first make a comprehensive study of the existing business problems, IT requirements, and network design. Next, they should develop solutions that will optimize the present architecture. This may entail redesigning several components of the network. It can also require the addition of a new data center.
In order to choose the correct design choices and technologies, network designers must gather the necessary information that will allow them to make a sound analysis during the planning stage. This also lets them correctly determine the new requirements that will support the company’s business goals. At this point, network designers typically utilize the decision tree and the decision matrix for easing and simplifying the process.
Progressive Office Cabling
Founded in 1986, Progressive Office’s success has been a direct result of years of commitment to seeking solutions on behalf of our clients in the Washington, D.C. and New York City areas. Efficiently working together, Progressive teams get cabling installed and operating as fast as possible while minimizing disruption and downtime. Call our toll free number (800) 614-4560 today.
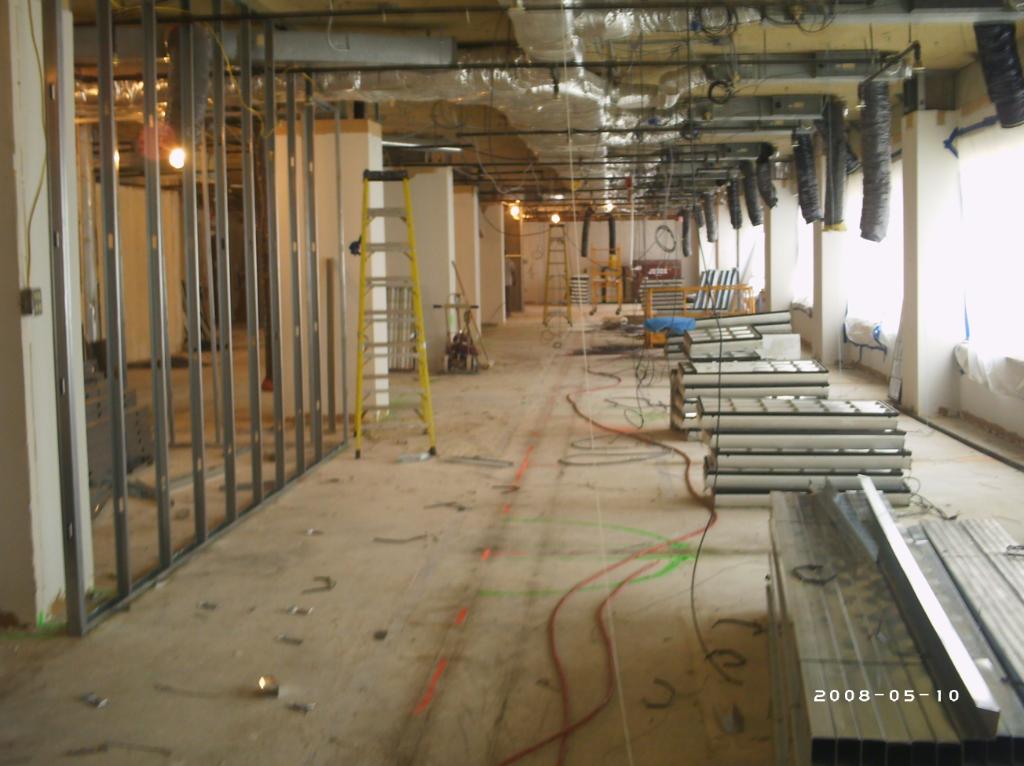



 As discussed in Part 1, office space has become very valuable and costly in many cities. Some companies will need to implement space optimization, and designing their
As discussed in Part 1, office space has become very valuable and costly in many cities. Some companies will need to implement space optimization, and designing their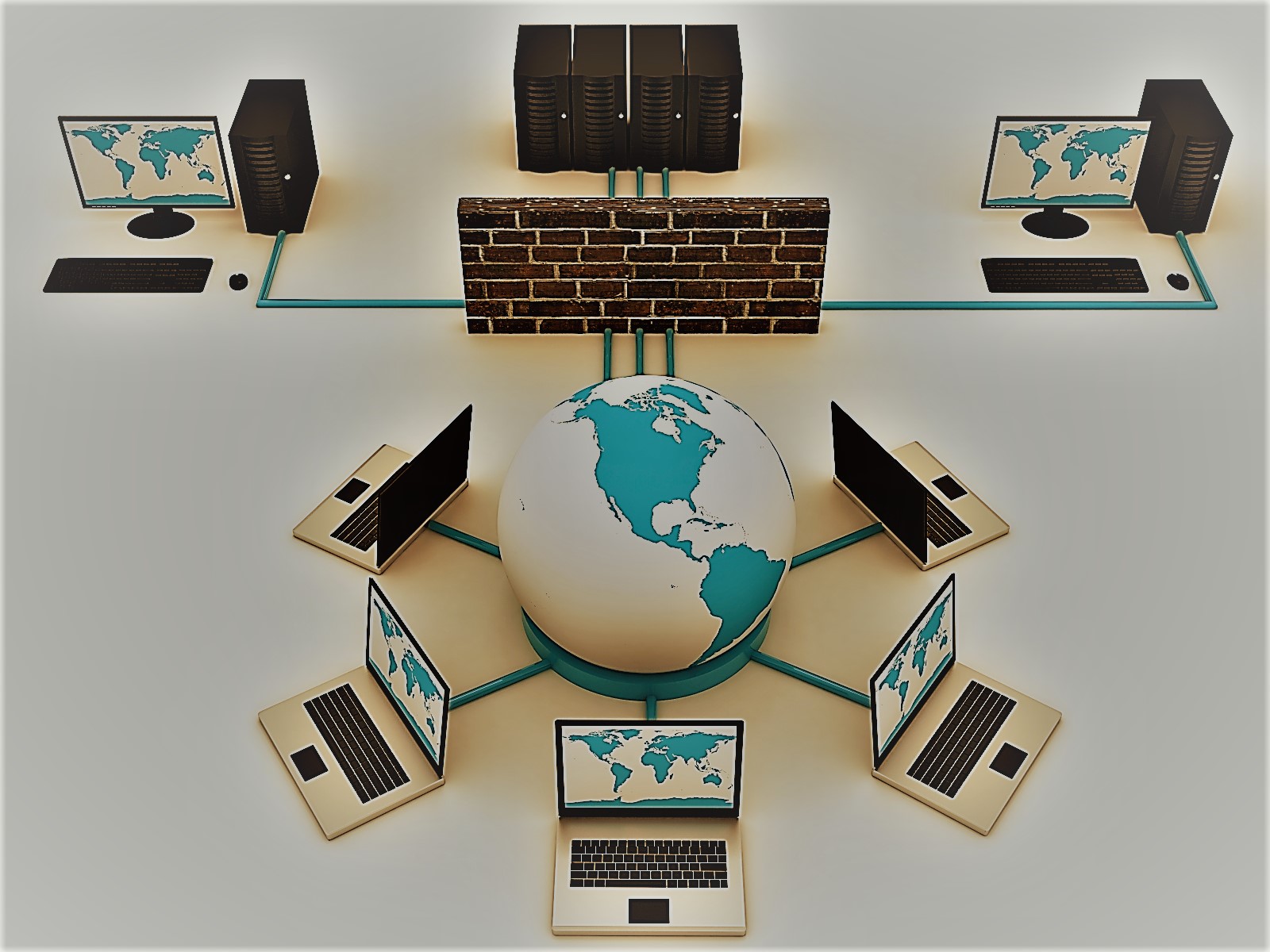 
 As discussed in Part 2, Top-Down Logic is used for the process of Preparation, Planning,
As discussed in Part 2, Top-Down Logic is used for the process of Preparation, Planning, 
 As discussed in Part 1, point-to-point cabling systems are outdated and companies should strongly consider making the transition to
As discussed in Part 1, point-to-point cabling systems are outdated and companies should strongly consider making the transition to  As previously discussed, the transition to IP-based security products and the rapid increase in business applications has resulted in end-users expecting greater video, audio, and data integration. These items require delivery over a standardized
As previously discussed, the transition to IP-based security products and the rapid increase in business applications has resulted in end-users expecting greater video, audio, and data integration. These items require delivery over a standardized 


 The quality of information flow is no better than the medium that carries it. This is the
The quality of information flow is no better than the medium that carries it. This is the 
 Riser cables were designed for non-plenum vertical applications like between the floors of multi-story buildings. They are also described as backbone cables. These
Riser cables were designed for non-plenum vertical applications like between the floors of multi-story buildings. They are also described as backbone cables. These 