
Data Center Cabling Best Practices – Part 1
 Modern data centers are equipped with devices and networking equipment that connect them. These devices demand increasingly greater bandwidth, and so their fiber or copper cabling must perform at a high level. Today’s data centers must be flexible, scalable, reliable, and manageable, making best practices required.
Modern data centers are equipped with devices and networking equipment that connect them. These devices demand increasingly greater bandwidth, and so their fiber or copper cabling must perform at a high level. Today’s data centers must be flexible, scalable, reliable, and manageable, making best practices required.
Planning the Infrastructure
Thus, documenting the existing and planned network, along with its equipment is needed. A flexible patching structure will permit the interconnection of devices at desired locations.
Structured Cabling
The structured approach of cabling revolves around the design of runs and connections that ease cable identification, maintenance, repair, and future expansion or reconfiguration. A Main Distribution Area (MDA) and Horizontal Distribution Area(s) (HDAs), along with two-post racks that permit improved access and cable management, will be needed.
MDA and HDA components must be of high quality and capable of bearing expected future loads. Their layout should have horizontal and vertical cable managers. The MDA contains primary cross-connects and core networking equipment. The HDA contains the cross-connects for the distribution of cables to Equipment Distribution Areas (EDAs). Patch cables will connect servers and storage by utilizing patch panels at their respective EDA.
Next, the equipment racks inside the data center must have their layout determined. A horizontal cabling configuration will be used for the distribution of cables from the HDA to the EDA. Flexible connectivity is required by a dynamic data center environment. The goal is the implementation of a system that transmits fiber channel, Ethernet, and other protocols.
Future port and application requirements will also need to be considered. Expansion and technological advances must be anticipated, so the installation of ports and cabling needed in the future should be done now to save on labor costs and downtime if upgrades are needed.
Structured Infrastructure Benefits
- Cable identification and fault isolation simplified
- Consistent cabling lays sound foundation for future
- Future expansions and modifications made easier
- Standard-compliant components from multiple vendors possible
- Flexible connections provided
Union Network Cabling
When union work requires a unionized cabling group, call on Progressive Office Network Cabling for your commercial Cat5e/6/6a and fiber cabling projects. Specializing in cabling for data, voice, security and even the latest WiFi and LiFi solutions. Phone: (202) 462-4290


 It is inevitable that applications requiring speeds greater than 100 Mbps and 1000 Mbps will increase. The growing use of wireless devices, high resolution images, HD video streaming, surveillance, and multimedia are straining the capacity of
It is inevitable that applications requiring speeds greater than 100 Mbps and 1000 Mbps will increase. The growing use of wireless devices, high resolution images, HD video streaming, surveillance, and multimedia are straining the capacity of 
 Nowadays offices and homes utilize either a wireless (Wi-Fi) connection or wired
Nowadays offices and homes utilize either a wireless (Wi-Fi) connection or wired 


 Punch-down
Punch-down 
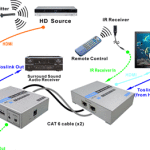 Data volume has grown extensively. Also, the processing capacity to users continues to get grow. Specialists in
Data volume has grown extensively. Also, the processing capacity to users continues to get grow. Specialists in 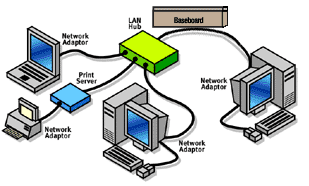
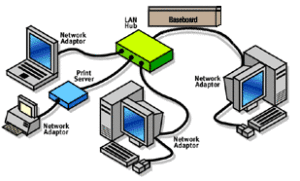 Be sure to purchase the correct components before you install a wired
Be sure to purchase the correct components before you install a wired 

 t connects personal computers to the wall plate or provides the short interconnects among the switches, routers and the patch panels in the wall closet or Server Room. These make use of stranded wires instead of solid to increase flexibility. It also lessens the risk of cracking when you unplug the cable. There is also a variety of Ethernet patch called the crossover cable. It is used to hook up two PCs together and sometimes to interconnect switches.
t connects personal computers to the wall plate or provides the short interconnects among the switches, routers and the patch panels in the wall closet or Server Room. These make use of stranded wires instead of solid to increase flexibility. It also lessens the risk of cracking when you unplug the cable. There is also a variety of Ethernet patch called the crossover cable. It is used to hook up two PCs together and sometimes to interconnect switches.