
Five New Approaches for Data Center Cabling – Part 2
 As discussed in Part 1, a properly designed network infrastructure is a prerequisite for being able to adapt emerging technology and support crucial systems cost effectively. Part 2 will discuss Modular Design, Optimized Network Infrastructure, and Virtualization.
As discussed in Part 1, a properly designed network infrastructure is a prerequisite for being able to adapt emerging technology and support crucial systems cost effectively. Part 2 will discuss Modular Design, Optimized Network Infrastructure, and Virtualization.
Modular Design
An approach that has recently gained traction is building new data centers capable of supporting the demand for excellent networking capability. Companies are increasingly participating during the construction phase by becoming more involved in decisions that help decrease costs. Specially designed and portable, modular data centers utilize engineered modules and components that offer the ability to scale and allow the creation of a converged infrastructure where necessary. Such modular designs are described as portable modular data centers or containerized data centers. Structured cabling is the foundation for every modular data center.
Optimized Network Infrastructure
According to data center providers, copper and fiber technology are sufficient for current networking infrastructure. However, there is a greater demand for more speed and streamlined connectivity for PCs, servers, and data storage. Optimizing data cabling is the method for achieving both. Optimized network infrastructure typically uses component standardization, including copper and fiber cabling, racks, and cabinets. Teamed with a physical-layer cable-management system, this approach results in a network that is both accessible and organized.
Virtualization
Research has found that more than half of small and medium-sized enterprises have their workloads running on virtual machines. In addition, more than 9 in 10 data center providers are now offering virtualization services to businesses. Proven to be scalable and cost-effective, virtualization technology is being commonly used for these four functions: desktop, server, network, and storage. As the popularity of IT infrastructure virtualization increases, ensuring that your organization has well-designed structured cabling will grow in importance.
Progressive Office Cabling
Founded in 1986, Progressive Office’s success has been a direct result of years of commitment to seeking solutions on behalf of our clients in the Washington, D.C. and New York City areas. Efficiently working together, Progressive teams get cabling installed and operating as fast as possible while minimizing disruption and downtime. Call our toll free number (800) 614-4560 today.


 The widespread use of fiber optic
The widespread use of fiber optic 
 Moving your company also means relocating and setting up its
Moving your company also means relocating and setting up its 

 As mentioned in Part 1, modern
As mentioned in Part 1, modern 
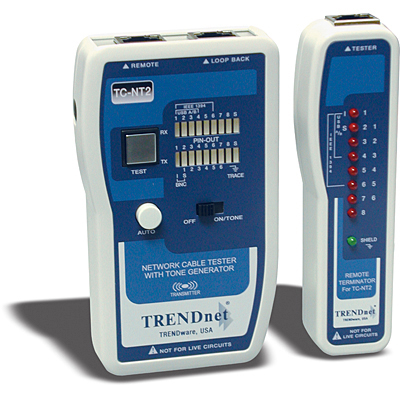

 Testing always plays a vital role in the process of installing new
Testing always plays a vital role in the process of installing new 
 Optical fiber
Optical fiber 

 will remain dominant in the structured cabling systems industry. This conclusion is based on analysis and forecasts made by several cabling installation companies worldwide. Both copper and optic fiber cabling are used for key structured cabling systems applications like LAN, data centers, and Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP). Optic fiber is gradually gaining in popularity, but copper cable still seems to be the major preference of most companies.
will remain dominant in the structured cabling systems industry. This conclusion is based on analysis and forecasts made by several cabling installation companies worldwide. Both copper and optic fiber cabling are used for key structured cabling systems applications like LAN, data centers, and Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP). Optic fiber is gradually gaining in popularity, but copper cable still seems to be the major preference of most companies.