Network Design Principles – Part 2
Reliable & Manageable Scaling
 Scalability is a crucial characteristic that must be considered by network designers.
Scalability is a crucial characteristic that must be considered by network designers.
In addition, a network should also be reliable and manageable, which promote stability. A network may be capable of expanding to several thousand routers. However, if there is a failure of some sort that causes instability due to greater processing and CPU usage required to compensate, the design won’t be successful.
A scalable network that is a challenge to manage or troubleshoot is also unacceptable.
Network problems that arise would take an excessive amount of time to address and repair, negatively impacting an organization’s business goals of the organization.
Thus, a scalable design must provide a manageable and reliable network.
Combining scalability, reliability, and manageability as the qualities of a network is a challenge. As a network expands, it becomes more complex, making management, maintenance, and repair more difficult.
Fault Isolation & Simplicity
Providing fault isolation boundaries creates fail-stop behavior for the wanted fault model. Fail-stop prevents faulty behavior from propagating past a fault isolation boundary. Effective network design must prevent a failure in one domain from spreading to other domains within a network. This is essential for the avoidance of unneeded processing and delays throughout the whole network because of a device or link failure. In addition, this will result in a converging network that has more stability, reliability, and speed.
The above concept also promotes simplicity as a network architecture characteristic, which decreases complexity in operations. Typically, fault isolation stops the propagation of network fault information across several domains or network areas. This will lead to greater network stability and the minimization of recovery time after failures.
The negative consequences due to a failure of a link or network node may spread to all devices across a network, resulting in a large volume of unneeded processing. A properly designed network using the Fault Domains Principle with its logical separation will limit the negative impact to within one fault domain.
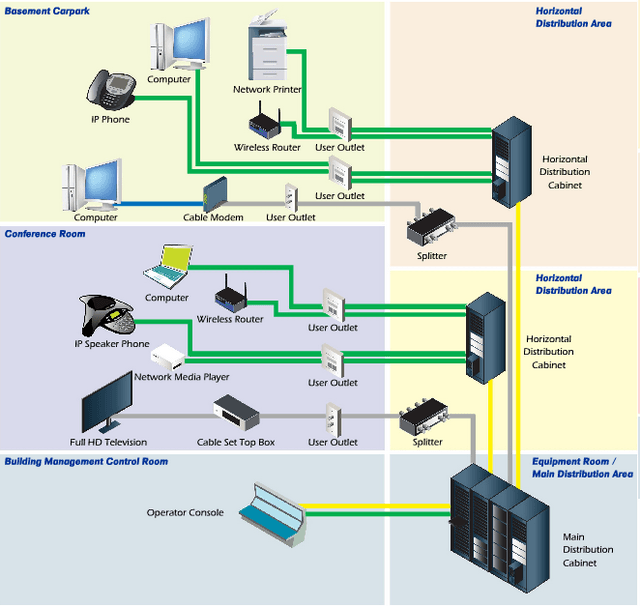
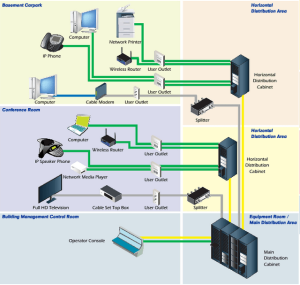
Progressive Office Cabling
Founded in 1986, Progressive Office’s success has been a direct result of years of commitment to seeking solutions on behalf of our clients in the Washington, D.C. and New York City areas. Efficiently working together, Progressive teams get cabling installed and operating as fast as possible while minimizing disruption and downtime. Call our toll free number (800) 614-4560 today.
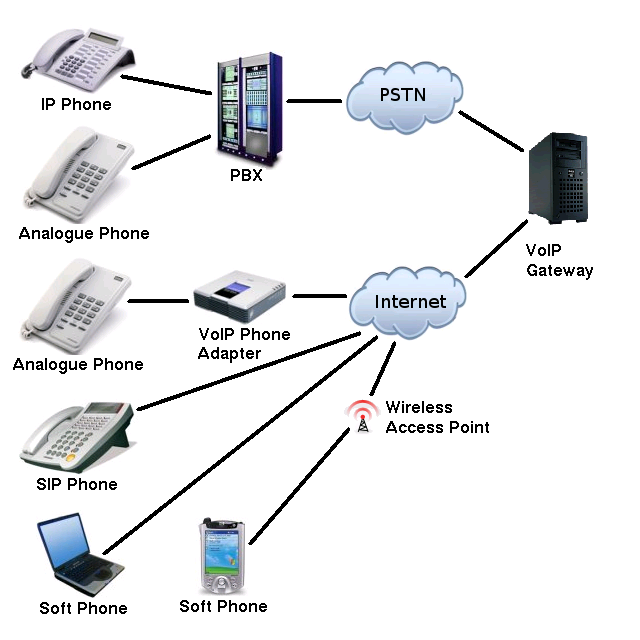


 The constraints of
The constraints of 
 As discussed in Part 3, a company’s
As discussed in Part 3, a company’s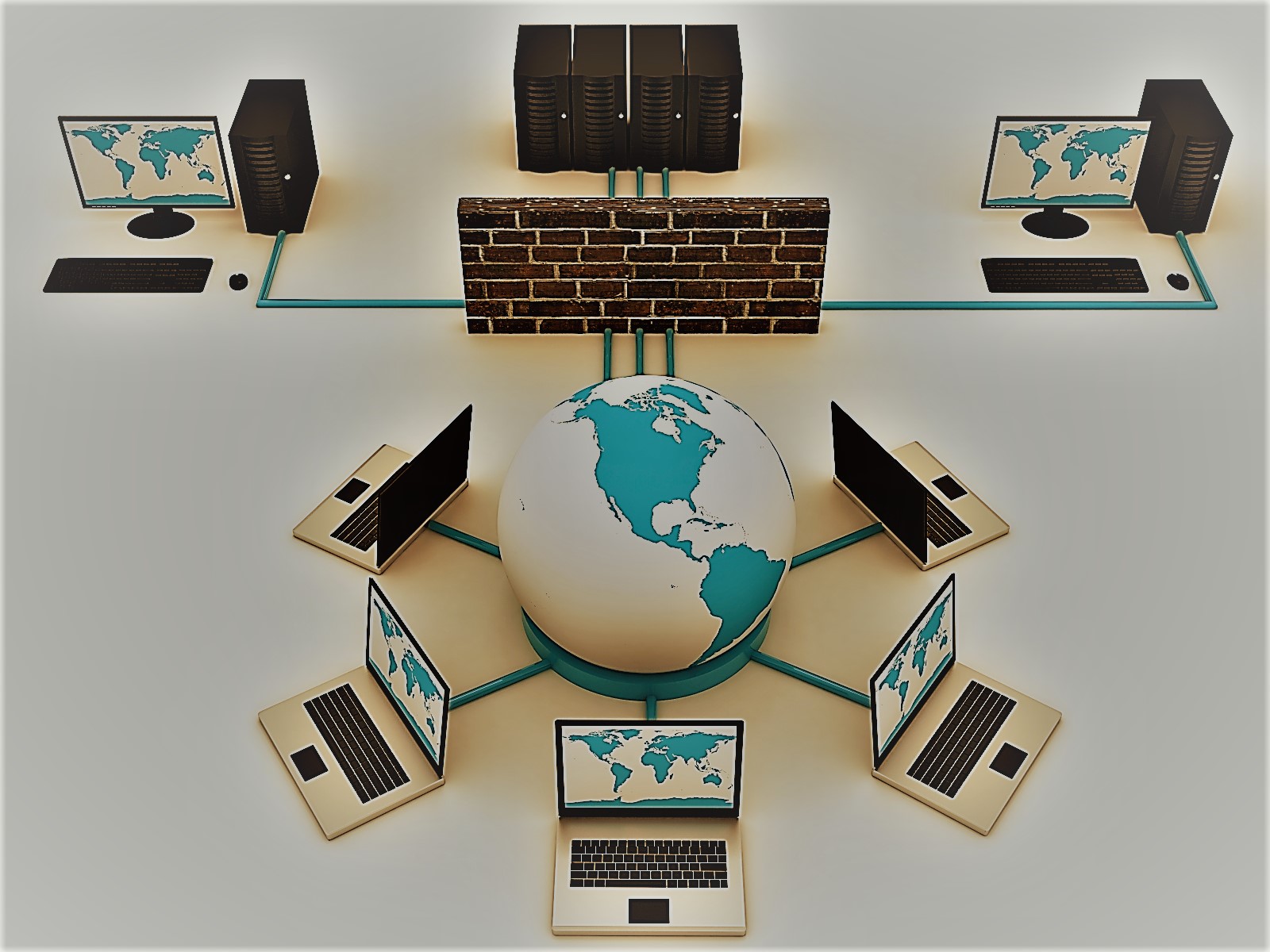 
 As discussed in Part 2, Top-Down Logic is used for the process of Preparation, Planning,
As discussed in Part 2, Top-Down Logic is used for the process of Preparation, Planning, 
 As discussed in Part 1, the Top-Down Approach for
As discussed in Part 1, the Top-Down Approach for