
Comparing Cat 7 to the Other Cats
 Nowadays offices and homes utilize either a wireless (Wi-Fi) connection or wired network connection. Usually faster than Wi-Fi, wired connections also have lower latency. These two types of network connection continue to progress technologically, providing users ever increasing speeds.
Nowadays offices and homes utilize either a wireless (Wi-Fi) connection or wired network connection. Usually faster than Wi-Fi, wired connections also have lower latency. These two types of network connection continue to progress technologically, providing users ever increasing speeds.
In the case of home networks, the speed of the internet connection is typically the issue, and the cabling may not be a factor. However, a company must consider the specifications of particular cables and how these would meet its requirements in order to properly decide which to select. There can be a vast difference between the network speeds of the various Ethernet cables.
Types
Cables are differentiated by standard categories. Category has been abbreviated to “Cat” by the industry. Currently, the most common cables in use are Cat 5, Cat 5e, Cat 6, and Cat 6a. The newest type is Cat 7. Every type is backward compatible, allowing users to insert a newer cable into a device that was manufactured for an older cable without any compatibility issues arising.
Progress
With every new cable category, users were provided increased speed and decreased crosstalk. Newer category cables provided faster speeds at increased lengths of cable. The following offers comparisons at 100 meters of cable, illustrating the differences between the ethernet cable categories:
Cat 5 - Considered slow and inadequate for business networks, providing up to 100 Mb/second at 100 Mhz.
Cat 5e - provides up to 1 Gb/second internet speed at 100 Mhz.
Cat 6 -provides up to 1 Gb/second, and cable lengths up to 55 meters can give internet speeds of 10 Gb/second at 250
Cat 6a -can provides speeds up to 10 Gb/second, to 100 meters of cable length, at 500 Mhz.
Cat 7 - provides speeds up to 10 Gb/second to 100 meters of cable, at 600 Mhz.
History
Cat 5 was the standard in 1995, Cat 5e became standard in 2001, and Cat 6 was introduced in 2002. Arriving in 2008, Cat 6a is typically the newest cable the majority of companies have used because it is not considered necessary to update to Cat 7 yet. Cat 7a and Cat 8, which were respectively released in 2010 and 2013, are still waiting in the wings.
Union Network Cabling
When union work requires a unionized cabling group, call on Union Network Cabling for your commercial Cat5e/6/6a and fiber cabling projects. We specialize in cabling for data, voice, security and even the latest WiFi and LiFi solutions. Phone: (202) 462-4290

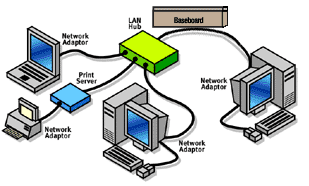
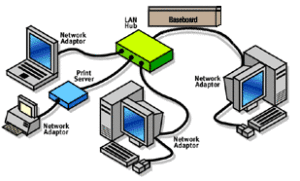 Be sure to purchase the correct components before you install a wired
Be sure to purchase the correct components before you install a wired 

