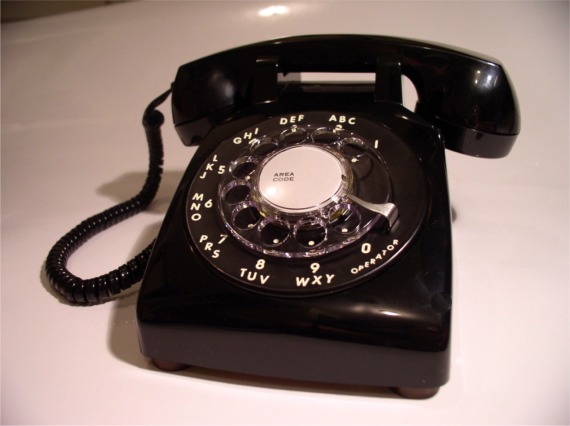

Microsoft is Ma Bell
Remember the 60s? I do. We had a rotary phone and it made phone calls. Our number was Whitehall 6-4990. And it was an amazing device that allowed us to talk to our friends and family by simply spinning the dial for each number and waiting for someone to pick up the phone on the other end. Back then, Ma Bell had a monopoly and most people probably thought that was fine. Phone service was reliable. The technology seemed like a blessing. The service was affordable although long-distance calls were very, very expensive.




 What is the difference between
What is the difference between 
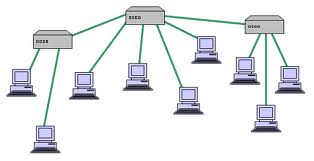
 One of the most important things about
One of the most important things about 

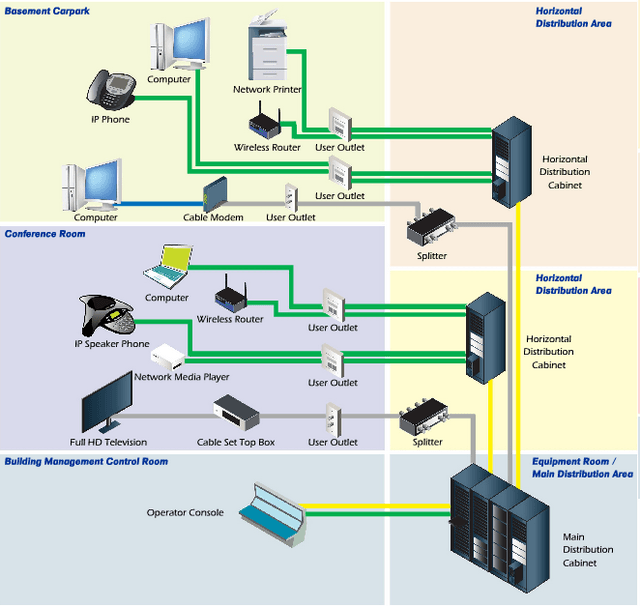
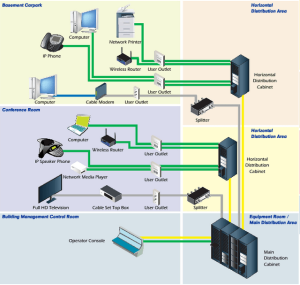 Structured cabling is a telecommunications
Structured cabling is a telecommunications