
The Advantages of Fiber Optic Cabling
 Sophisticated technology has made it possible for the new generation of entrepreneurs to enjoy Cat5, Cat6, and fiber optic cabling. These technologies amplify speed, enhance performance and reduce costs.
Sophisticated technology has made it possible for the new generation of entrepreneurs to enjoy Cat5, Cat6, and fiber optic cabling. These technologies amplify speed, enhance performance and reduce costs.
Cat5
Cat5 refers to structured cabling for transmission of data signals. This is used primarily for computer networks. Standard performance is a maximum of 100 MHz and fits into the Gigabit and Fast Ethernet. Cat5 carries other signals for video and telephony. Almost all Cat5 cables are unprotected and depend on balanced lines and twisted pair designs as well as differential signals to reject noise.
Cat6
Cat6 is considered standard for Gigabit Ethernet along with network protocols that require more speed than Cat5 cables. Cat6 is made up of four pairs of wires comparable to Cat5. Using all four pairs allows this model to support communications that are double the speed of Cat5. This translates to speeds of one gigabit/second.
Fiber Optic Cabling
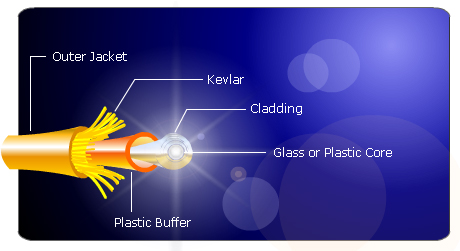
Fiber optic cabling or optical fiber is distinct from Cat5 and Cat6. It utilizes light rather than electricity to transmit signals. It has a better signal compared to the traditional copper cables, so it sends signals more rapidly than is possible with copper cable. Optical fiber is also impervious to interference from electricity, which means that users can use it anywhere and anytime. Fiber optic cabling also allows for much longer transmission distances. Cat5 and Cat6 are limited to only 100m of cable from wallplate to computer.
Even telephone companies have started to phase out copper wires in favor of fiber optic cables. Technical experts of these firms are working to reduce the vulnerability of fiber optic cables to water. Using fiber optic provides enterprises the adaptability of augmenting bandwidth in just several days compared to the conventional copper circuits, which usually take a maximum of one month to upgrade. Fiber optic connections generally start at two megabytes, with dedicated upload and download speeds of up to one gigabyte.
Fiber Connection
The fiber connection will also facilitate the business-mode Service Level Agreement or SLA. This implies that business entities obtain a secured 99.99 percent uptime. If power failure and other issues occur, technical specialists can conduct repairs within a maximum period of four hours. Your business reaps the benefits of speed, assured uptime and fast service by a reputable company like Progressive Office Cabling. It makes use of high-quality cables along with connectivity parts as well as the most efficient systems in cable management. The company’s technicians have been trained properly to be able to respond to your demands. With a proven project management approach, effective communication is guaranteed during the entire project.
This kind of service is practically unmatched in this industry. Savvy users and business proprietors will know how to choose the service provider that can deliver solutions based on their requirements.

 An efficient
An efficient 



 One of the most important things about
One of the most important things about 
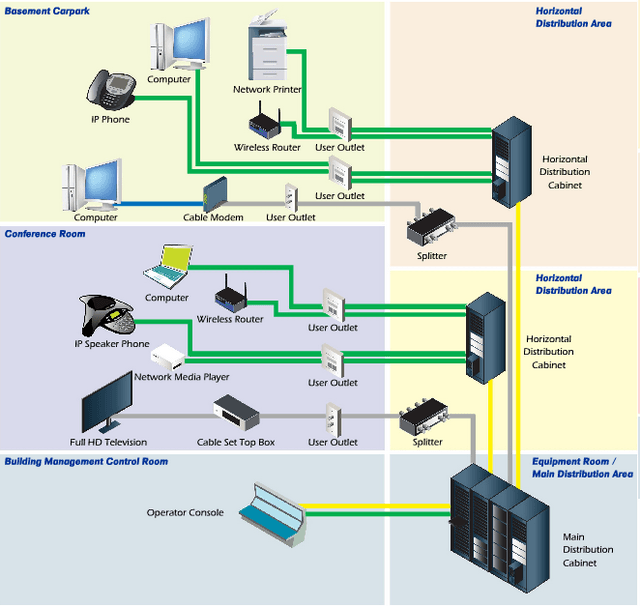
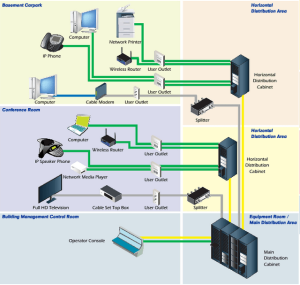 Structured cabling is a telecommunications
Structured cabling is a telecommunications 
 No, it’s not ET calling home. “Alien Crosstalk” is defined as “unwanted signal coupling from one balanced twisted-pair component, channel, or permanent link to another”.
No, it’s not ET calling home. “Alien Crosstalk” is defined as “unwanted signal coupling from one balanced twisted-pair component, channel, or permanent link to another”.