How Improper Cabling Causes Network Issues – Part 1
 Your employees are dissatisfied by their company’s network performance, and it is affecting their productivity. A number of factors must be taken into consideration. How many users are attempting to use resources simultaneously? Have you taken into account how much the use of devices has grown? Is your network equipment sufficient to meet demand? Answering the above questions will help, but network issues may be directly related to your company’s structured cabling.
Your employees are dissatisfied by their company’s network performance, and it is affecting their productivity. A number of factors must be taken into consideration. How many users are attempting to use resources simultaneously? Have you taken into account how much the use of devices has grown? Is your network equipment sufficient to meet demand? Answering the above questions will help, but network issues may be directly related to your company’s structured cabling.
Outdated Cabling
In many instances, the age of your structured cabling system may be responsible for poor network performance. 15-year-old cabling may have met standards when it was installed, but now it may be unable to handle the ever increasing network traffic needs of your company.
An internet service provider (ISP) provides the cable that provides the connection from your company’s network to the internet. When this backbone component fails to meet today’s bandwidth standards, bottlenecks may occur.
In situations where you are attempting to operate at speeds that are too high or carry excessive bandwidth via a cable that not rated for the capacity, it will be noticeable to users and their productivity will decline, hampering business operations.
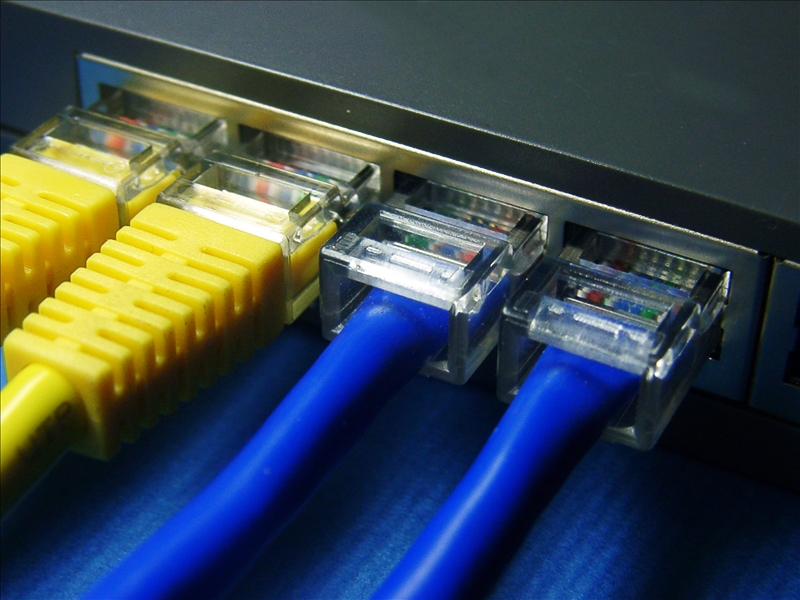
Quality of Cabling
Cabling manufacturers rate their cables in terms of capability and performance. For example, CAT6 and CAT6a cabling have different capabilities, CAT being an abbreviation for category. A manufacturer must meet the performance standards set by the Telecommunications Industry Association (TIA) for each category of cabling.
Cabling that exceeds minimum standards will attain higher network speeds without having to upgrade your cabling. In contrast, for cabling that only meets the minimum standards, the company network speed will be unable to expand much beyond the rating of the cable.
It is helpful to understand cable standards and ratings. Even though a cable is labeled Category 6A, it is not automatic that it meets the minimum performance standards of this category. The brand name and manufacturing quality will play a big role in the cable’s output.
Part 2 will discuss Compatibility, Patch Cords, and Poor Installation.
Progressive Office Cabling
Founded in 1986, Progressive Office’s success has been a direct result of years of commitment to seeking solutions on behalf of our clients in the Washington, D.C., Atlanta, Pittsburgh and New York City areas. Efficiently working together, Progressive teams get cabling installed and operating as fast as possible while minimizing disruption and downtime. Call our toll free number (800) 614-4560 today.
;


 Testing always plays a vital role in the process of installing new
Testing always plays a vital role in the process of installing new 