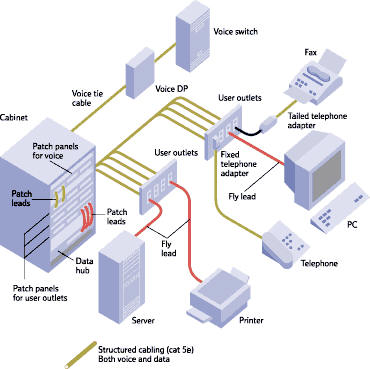
Powerful Networks in Structured Cabling
 It is known that structured cabling systems are fabricated to guarantee that information flows efficiently through the network. Such system are made up of transmission products installed based on appropriate guidelines in engineering design. These enable users to put into operation voice and data systems that capitalizes on speed.
It is known that structured cabling systems are fabricated to guarantee that information flows efficiently through the network. Such system are made up of transmission products installed based on appropriate guidelines in engineering design. These enable users to put into operation voice and data systems that capitalizes on speed.
This particular configuration has emerged as shared platform for multiple information technology applications. These include voice and data, building automation, security mechanisms, telecommunications conferencing, and fire alarms. This union transformed the structured cabling platform into the most essential network element. Therefore, it calls for a crucial investment in a very reliable, adaptable and scalable cabling structure.
High-performance Networks
This efficient and complex cabling scheme segregates the whole infrastructure into controllable blocks. After that, it puts them together to come up with a high-performance network. This end product is the vital link for many enterprises and all data hubs. Such a system facilitates consistency across the network particularly for commercial building structures. Consistency generates cost-effectiveness by standardizing maintenance processes, cutting down on manpower requirements, and improving reliability.
The “structured” design makes possible easy management by identifying specific distribution points, regular labeling and color codes, cabling management, and distribution techniques. As a rule, data facility managers use dynamic methodologies to fill the center with information technology equipment. This accommodates the evolving needs of business operations which frequently compel the need for the most modern IT equipment. Since companies rely on equipment as well as infrastructure, management believes requirements for additional IT capability should be made promptly. If the infrastructure is below par, upgrades will be much more difficult.
Crucial Concerns
The best IT specialists see to it that problems in structured cabling systems are dealt with immediately. One of the primary concerns is to employ highly competent service providers and coordinate entry points/space for each provider. This procedure enhances flaw tolerance of the overall system design. The high-performance model supports aggregate telecommunications requirements and thereby leads to a maximum returns on investments.
Centralized Intermediate Distribution Frames (IDFs) should be in centralized locations in the office facility. This will produce efficient cable management and will ease the addition of new equipment. This design technique has been adopted to avoid any disruption of the data unit or minimized once changes or upgrades are implemented. Telecommunications rooms contain the IDFs, main distribution frames and entrance facilities. Switches are installed in the middle of server rows for economical management.
Please contact us if you have any questions or concerns about your office network cabling.

Patch Cables and Twisted Pair Cabling
The patch cable is used to link up two network devices. This type of cabling is usually a Cat6 or a Cat5e cable tha t connects personal computers to the wall plate or provides the short interconnects among the switches, routers and the patch panels in the wall closet or Server Room. These make use of stranded wires instead of solid to increase flexibility. It also lessens the risk of cracking when you unplug the cable. There is also a variety of Ethernet patch called the crossover cable. It is used to hook up two PCs together and sometimes to interconnect switches.
t connects personal computers to the wall plate or provides the short interconnects among the switches, routers and the patch panels in the wall closet or Server Room. These make use of stranded wires instead of solid to increase flexibility. It also lessens the risk of cracking when you unplug the cable. There is also a variety of Ethernet patch called the crossover cable. It is used to hook up two PCs together and sometimes to interconnect switches.
Ethernet Systems
Ethernet systems ensure adaptable and economical methods of conveying voice, data, and multimedia over integrated networks. In fact, Ethernet patch cords have become very common. These wall to wall cables gave rise to the growth of generic and structured cabling systems. Today, these are used practically for all networking components regardless of industry or application. However, there are concerns that you need to consider. Whereas modular attributes and profusion of patch cables denote absolute universal use, there are differences that can reduce interchangeability. Some of the disparities originate from various wiring configurations of cable conductors and connector pins.
Twister Pair Cables
For this type of cabling, two conductors are coiled to prevent electromagnetic interference (commonly known as EMI) that comes from external (usually electrical) sources. One example is the electromagnetic radiation caused by uncovered twisted pair cables or UTP as well as cross talk produced by adjacent electrical wires. The process of shielding generates a conductive barrier to lessen these electromagnetic waves. It also creates a conduit for conduction so that currents and data can traverse freely. Shielding can be applied on individual pairs or as a group of pairs.
Twisted conductor pairs form a secure circuit. The voltages carry the same magnitude or amplitude. However, one is positive while the other is negative. Incidentally, crosstalk takes place if the electromagnetic field turns out a signal that is too big or strong and intereferes with a nearby pair. The sound is like a fusion of the two fields by means of a swap of the energy between them. Certain components of these signals are passed on to each other during this exchange of energy.
As a result, here is an ensuing increase in the level of “noise”. External sources of EMI and RFI create signal interference in a similar manner. These cause distortion of the signals that go to your office and communications equipment.
Overall, these are the things that you should take into account with regards to twisted and patch cabling.
Please feel free to contact us if you need help with your office cabling project!

Cabling Tips for Security Cameras
Cabling is definitely not the showy part of any security system. Nevertheless, it is an essential component of the system. It may seem complicated. There are many considerations in choosing and installing cables to ensure that the security system functions properly. Cables basically provide power for camera installation and transmit signals going back to the digital video recorder (DVR).
is definitely not the showy part of any security system. Nevertheless, it is an essential component of the system. It may seem complicated. There are many considerations in choosing and installing cables to ensure that the security system functions properly. Cables basically provide power for camera installation and transmit signals going back to the digital video recorder (DVR).
Deciding on the Perfect Cabling
Find out whether the system is analog (alternating current frequency has been modified) or digital (electronic technology). Then, you can figure out the proper cable for installation of your security cameras. Or simply refer to the manufacturing specs on the camera system.
The second step is to determine if your camera is powered remotely or connected to a nearby power outlet. It may be necessary to combine power and video cables. Security power and video cables can run next to each other or within one cable jacket. This makes installation easier by pulling one instead of two separate wires.
Make sure to test the cable before you install the CCTV. Examine each cable at the DVR position just to make sure that the cables are working prior to installation.
Cabling Guidelines
Quite often security cameras require coaxial cables to send video from the camera to your recorder. With the RG59 type of coax cable, it is possible to position the camera up to 600 feet away. The RG6 coax cable, on the other hand, may be extended up to 1,000 feet. Cut the cable according to your preferred length but leave an extra service loop of 10 – 20 feet for future flexibility.
What are the steps to follow?
- Make the necessary BNC connection on the cable. This is a small quick round connector primarily for coaxial cables.
- Plug one end of the BNC cable to the camera and the other to your DVR.
- Strip the shield of the power cable to expose the black and red wires. Then, remove the jacket (at least ¼ inch) from each wire.
- Put the wires inside the terminal block at the end of the female power wire plait. It should be red on red wires and black on black wires. Tighten screws on the terminals. Plug the camera into the fitting at the side of the braid.
- Attach wires directly to the positive and negative leads respectively in the power box. Red wire is for positive while black is for negative. This is applicable if you will connect the camera to a multiple camera power supply unit.
- In case you will attach the camera to a single power unit, connect the male power wire braid as well as power supply to the tip of the tress.
Now, the installation is complete and you are ready to use the system.

Designs of Optic Fiber Cables
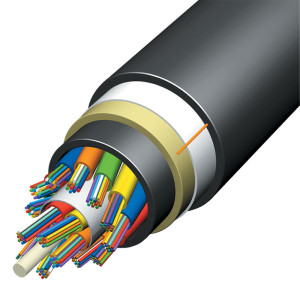 Optical fiber cabling is made up of a fiber core and a protective layer. The shield is typically coated with a polymer. It protects the cable from damage and does not contribute to optical wave guide properties. The coated fiber is a durable synthetic resin serving as a support for the cable’s core. Protective jacket layers are added depending on the cabling application.
Optical fiber cabling is made up of a fiber core and a protective layer. The shield is typically coated with a polymer. It protects the cable from damage and does not contribute to optical wave guide properties. The coated fiber is a durable synthetic resin serving as a support for the cable’s core. Protective jacket layers are added depending on the cabling application.
Fiber over Copper
Fiber has benefits over copper. Fiber optic transmission does not emit Radio Frequency Interference or RFI. This guarantees secured communications since light waves can't be easily intercepted. On the contrary, copper wires give off signals that interfere with other electronic equipment. That is why utility firms now run power lines with fibers

Unique Properties of Fiber Optic Cabling
 Fiber optics is capable of resolving many issues in data communications. However, computer data is normally transmitted over ordinary copper cables because it's adequate at lower speeds and shorter distances. It is not advisable to utilize fiber cable in these ordinary instances because of the high costs.
Fiber optics is capable of resolving many issues in data communications. However, computer data is normally transmitted over ordinary copper cables because it's adequate at lower speeds and shorter distances. It is not advisable to utilize fiber cable in these ordinary instances because of the high costs.
Fiber is impervious to electromagnetic interference because the signals are transmitted as light impulses. That means that Electromagnetic Interference (EMI) is not possible. Light waves are not effected by magnetism. This type of impediment can happen in coaxial and Cat5/6 cables because electricity can interfere with data signals over copper wires. Magnetic fields produce electrical current and this electromagnetic Interference is noise that can scramble data.
Fiber optic cabling also is much better at providing security of data since electromagnetic fields are not emitted around optical fibers. The data is restricted within the structure of the cable making it impossible to tap signals being communicated without cutting across the fiber. Emissions can not be easily intercepted. Hence, the fiber is by far most secure channel for carrying sensitive data.
Fiber is also a “non-conductive cable” because there is no metal in its design. It's a highly purified glass fiber. While copper is a conductive cable that can attract power surges and unwanted current. With fiber, outdoor varieties are costly because these call for special strength. Therefore, fiber optic cable is usually more cost-effective for indoor use. With copper, it is also important to get rid of the current commonly known as ground loop. The metal cable can run into signal transmission distortions due to slight transmissions in electricity.
Fiber optics also does away with threats coming from sparks. The transmission of signals can be hazardous because of this phenomenon. Although the spark itself is not dangerous, it can lead to greater problems especially in industrial and chemical plants where the air is polluted by possibly dangerous vapors. Fiber cable does not generate sparks because it carries no electrical current.
Installation of fiber is less difficult because of its small size and flexibility. And fiber optic cables can pass along the same route as electric cable without producing any noise. The size, lightness and elasticity of fiber optic cables also makes them suitable for short-term or portable installations. And they transmit signals over longer distances too. Amplifying the transmission capability of copper wire cables makes them more unyielding. Thicker copper cables are also hard to mount in spaces where the cables have to pass through cable conduits and concrete walls.
Fiber optic means higher bandwidth too. It has the capability to transmit high-speed signals over lengthy distances without repeaters, unlike copper cables. The fiber optic’s range is not infinite but it is way more than copper cable.
If you need help in figuring out the ideal cabling topology, contact us or call 202-462-4290 for a free on-site survey and proposal.

Essential Facts About Cabling System
 Your office cabling system is costly and complicated investment. It's also a commitment to an office design and structure that is not easy to modify. If you add more workstations later, new cabling might be needed.
Your office cabling system is costly and complicated investment. It's also a commitment to an office design and structure that is not easy to modify. If you add more workstations later, new cabling might be needed.
Most offices have a structured cabling topology that hardwires the cables from wallplate to patch panel. With this system, modifications are less likely because the initial installaiont includes a planning process that should anticipate some expansion. By pre-wiring potential locations in an existing or newly-constructed building, future moves, additions or alterations are avoided. You can just transfer patched cables in the wiring closet. Also, it is critical to number the wallplates to match the corresponding patch panel number. This will make it much easier to relocate a workstation or to troubleshoot a connectivity problem.
There are several sub-systems to consider:
- The Demark refers to the point where the Internet Service Provider's (ISP) data line comes to an end and hooks up with the cabling in the building.
- The equipment room serves as storage for all apparatus and wiring integration points.
- Backbone cabling are high-speed cables (typically Cat6 or fiber) that connect various floors or wall closets.
- The horizontal cabling for links up the network space to individual wallplates. These are done through conduits and ceiling spaces on every level.
- The telecommunications enclosures are wall or floor mounted cages that hold the network equipment; primarily the patch panels ands switches but also sometimes the server and Uninterruptible Power Supplies (UPS) too.
Installation and design of structured cabling is regulated by standards that identify the following:
- Network data switches
- Offices layout for voice & data communications for Cat5e or Cat6 cable
- Fiber Optic cables for backbones
- Modular connectors at the wallplate
These components will guide the layout of cables in order to fulfill the data access requirements of your office. All of the cables start at the patch panel on a mounted rack (about 19 inches wide) in the wall closet. From there, they traverse through the drop ceiling and down the walls to individual wallplates. Quite often a wallplate will host 2 or more connections. At the wallplate a short patch cable, usually 7 to 14 feet in length wil connect the computer, phone, printer or other networked device.
All cabling standards require that all of the eight conductors in Cat5, Cat5e and Cat6 cables are inter-connected in a precise color-coded pattern. The network cable connects each device but some devices can share a single cable. This is true for VoIP phones. Most VoIP phones have a jack for the network cable and then a jack on the phone for connecting the computer. This pass-thru enables the two devices to share one connection.

Benefits of Copper Cabling Solutions
 The conventional process of copper cabling has been used for several years and is still preferred by many network cable providers and end-users. Companies like Progressive Office Cabling offer a complete range of cabling solutions in Cat5, Cat5e, Cat6a and Cat6, providing clients with high-quality cable as well as connectivity components. Progressive Office Cabling makes use of highly effective cable management systems and well-trained technicians for installation jobs. It also employs a web-based online project management system to guarantee proper implementation and monitoring of any project.
The conventional process of copper cabling has been used for several years and is still preferred by many network cable providers and end-users. Companies like Progressive Office Cabling offer a complete range of cabling solutions in Cat5, Cat5e, Cat6a and Cat6, providing clients with high-quality cable as well as connectivity components. Progressive Office Cabling makes use of highly effective cable management systems and well-trained technicians for installation jobs. It also employs a web-based online project management system to guarantee proper implementation and monitoring of any project.
How Does Copper Cabling Work?
Installation technicians have to follow specific policies and standards, particularly when it comes to building structure concerns. There are several steps to follow with regard to installation. First, the cable should have the appropriate covering or insulation, which is normally made of PVC, Plenum, Ultra-Violet, or mold-resistant varieties. The cable is cut according to the needed length, and outer covers are removed before connectors are attached. Use the appropriate stripping tools for this purpose. Cables should be mounted as orderly as possible.
There are instances when installers have to use ladder trays and J-hooks, which are made for network cabling, or shoot nails into concrete ceilings using a tool that literally propels nails like bullets into the concrete surfaces. Network cables must be installed away from electric power lines, fluorescent lamps and industrial machines; the risk of electrical coupling can increase dependent on proximity and voltage factors.
Different Benefits
Copper cabling has multiple benefits and is the most effective conductor out there. Copper cables are flexible, which is especially advantageous if you are using electrical wires. It is necessary to bend the wire during installation, so you need something durable that will not easily break after a lot of twisting. Copper does not easily melt, so even if a sudden surge of current or overload takes place, there is no risk of burning or melting. At the same time, copper is not difficult to work on. The majority of electricians opt for copper wires because they can be stripped easily or pulled through rigid spots.
With regard to structured copper cabling, there is the Power over Ethernet benefit. This means that it is possible to run power through devices such as Wireless Access Points, surveillance cameras, and power phones. There is an emergency power supply that continues to power mission-critical devices even if electrical power conks out. Copper cabling supports modern technologies and facilitates the convergence of different applications. Hence, it is important that copper cabling is optimized for your requirements. That is why you should make sure to get the services only of experienced and trustworthy providers in the industry. Choose the provider that ensures customer satisfaction and warranty after installation.

The Advantages of Fiber Optic Cabling
 Sophisticated technology has made it possible for the new generation of entrepreneurs to enjoy Cat5, Cat6, and fiber optic cabling. These technologies amplify speed, enhance performance and reduce costs.
Sophisticated technology has made it possible for the new generation of entrepreneurs to enjoy Cat5, Cat6, and fiber optic cabling. These technologies amplify speed, enhance performance and reduce costs.
Cat5
Cat5 refers to structured cabling for transmission of data signals. This is used primarily for computer networks. Standard performance is a maximum of 100 MHz and fits into the Gigabit and Fast Ethernet. Cat5 carries other signals for video and telephony. Almost all Cat5 cables are unprotected and depend on balanced lines and twisted pair designs as well as differential signals to reject noise.
Cat6
Cat6 is considered standard for Gigabit Ethernet along with network protocols that require more speed than Cat5 cables. Cat6 is made up of four pairs of wires comparable to Cat5. Using all four pairs allows this model to support communications that are double the speed of Cat5. This translates to speeds of one gigabit/second.
Fiber Optic Cabling
Fiber optic cabling or optical fiber is distinct from Cat5 and Cat6. It utilizes light rather than electricity to transmit signals. It has a better signal compared to the traditional copper cables, so it sends signals more rapidly than is possible with copper cable. Optical fiber is also impervious to interference from electricity, which means that users can use it anywhere and anytime. Fiber optic cabling also allows for much longer transmission distances. Cat5 and Cat6 are limited to only 100m of cable from wallplate to computer.
Even telephone companies have started to phase out copper wires in favor of fiber optic cables. Technical experts of these firms are working to reduce the vulnerability of fiber optic cables to water. Using fiber optic provides enterprises the adaptability of augmenting bandwidth in just several days compared to the conventional copper circuits, which usually take a maximum of one month to upgrade. Fiber optic connections generally start at two megabytes, with dedicated upload and download speeds of up to one gigabyte.
Fiber Connection
The fiber connection will also facilitate the business-mode Service Level Agreement or SLA. This implies that business entities obtain a secured 99.99 percent uptime. If power failure and other issues occur, technical specialists can conduct repairs within a maximum period of four hours. Your business reaps the benefits of speed, assured uptime and fast service by a reputable company like Progressive Office Cabling. It makes use of high-quality cables along with connectivity parts as well as the most efficient systems in cable management. The company’s technicians have been trained properly to be able to respond to your demands. With a proven project management approach, effective communication is guaranteed during the entire project.
This kind of service is practically unmatched in this industry. Savvy users and business proprietors will know how to choose the service provider that can deliver solutions based on their requirements.
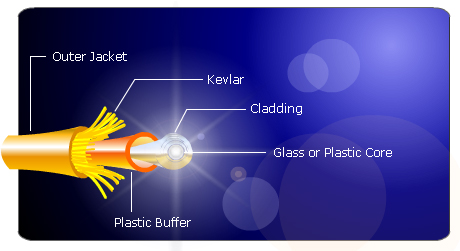
About Fiber Optic Cabling
 An efficient cabling system is one of the prerequisites for a functional network and is considered to be an investment that will comply with your networking needs in the long term. Fiber optic cabling is the product of modern technology. This type of cabling conveys information from one location to another through pulses of light in an optical fiber. It is important for users to learn the advantages of fiber optics.
An efficient cabling system is one of the prerequisites for a functional network and is considered to be an investment that will comply with your networking needs in the long term. Fiber optic cabling is the product of modern technology. This type of cabling conveys information from one location to another through pulses of light in an optical fiber. It is important for users to learn the advantages of fiber optics.
Fiber optic cables possess more bandwidth, or communications capacity, compared to metal and copper wires. This variety can transmit more information with greater reliability, which is one of the reasons for cable television and telephone providers to opt for fiber. The optical fiber also generates minimal power loss, thereby allowing longer transmission. Such cables are resistant against electromagnetic interference; they can operate in loud electrical environments because the interference does not have any effect on fiber cables.
Moreover, data moves at higher speeds since the fiber optic signal ensures that only a small amount of signal is lost in the course of transmission. Data is safe with fiber cables. It does not give off signals and is relatively hard to utilize. You will easily find out if the cable has been tapped or infringement has been made on the system, as this tampering causes the cable to give away light and causes the whole system to break down. Fiber optic cabling allows users to store electronics and hardware in a particular area rather than wiring cabinets with equipment.
Fiber optic cabling facilitates consistent transmission of data. The central part is fabricated from glass, an insulator, so that electricity cannot pass through. It is barely affected by ebb and flow of temperature, unlike copper, and can be immersed in water without any negative effects. Fiber optic is lightweight and thread like, but tougher than copper wiring. Specifications are a lot more than the copper cable. Although it is more difficult to terminate compared to copper, modern connectors make it easier to terminate.
The costs of fiber as well as other components are decreasing gradually but installation is more costly. Of course, fiber is more expensive than copper but it become more cost-effective in the long run due to less required maintenance, networking and downtime.
Practical users value their money. There may be certain downsides, such as installation expenses, but these are decreasing steadily each year. Fibers are also prone to damages because of the fine and smaller strands. Nevertheless, you can always institute safeguards that will address these points. Make it a point to determine the benefits of using fiber optic cabling. Install the highest quality of optic fiber cabling that your financial resources will allow.

