
The 5 Most Common Structured Cabling Errors – Part 1
 Structured cabling systems are so standardized that good practices should merely entail following ISO/IEC, CENELEC or Telecommunications Industry Association (TIA) documentation for panel and outlet standards, cable pathway standards, maximum cable and patch cord lengths, patch testing standards, etc. Strictly doing so will invariably result in an installation that is professional and trouble free. In addition, as data speeds grow faster and faster, following industry standards becomes even more crucial.
Structured cabling systems are so standardized that good practices should merely entail following ISO/IEC, CENELEC or Telecommunications Industry Association (TIA) documentation for panel and outlet standards, cable pathway standards, maximum cable and patch cord lengths, patch testing standards, etc. Strictly doing so will invariably result in an installation that is professional and trouble free. In addition, as data speeds grow faster and faster, following industry standards becomes even more crucial.
Improperly installed cabling made up of shorter runs, which do not overly stress the system, may function well enough. In addition, data speeds may be quite beneath the cable specification capacity. As an example, CAT5e carrying 100Mbps and capable of 1Gbps will have ample margin of error. However, structured cabling systems still need qualified technicians for proper installation supporting maximum data speeds over the entire network as required.
The following will discuss the five most common errors of structured cabling. Remember to call an experienced and expert cabling installation team to get the best results for your company’s project.
Error No. 1
Considering cables as merely wiring is the first error. They are actually very important electronic components that provide the pathway for data from point to point within a network. These points may be a desktop PC, a network switch, server, router, and wireless access point. When you consider that cables make these connections possible, then you can understand how important it is to make sure that the cabling is of high quality and properly installed.
Error No. 2
Running data cables near power cables is the second error. Even when cables are screened, this practice is unsound. When data cables are running near and parallel to power cables, noise emitted by power cables may infiltrate data cables. As the load carried by power cables fluctuate, resulting spikes or surges may radiate into the data cables, creating undesired noise decreasing the quality of the data transmission.
Part 2 will discuss three more common errors of structured cabling.
Progressive Office Cabling
Founded in 1986, Progressive Office’s success has been a direct result of years of commitment to seeking solutions on behalf of our clients in the Washington, D.C. and New York City areas. Efficiently working together, Progressive teams get cabling installed and operating as fast as possible while minimizing disruption and downtime. Call our toll free number (800) 614-4560 today.


 The widespread use of fiber optic
The widespread use of fiber optic 
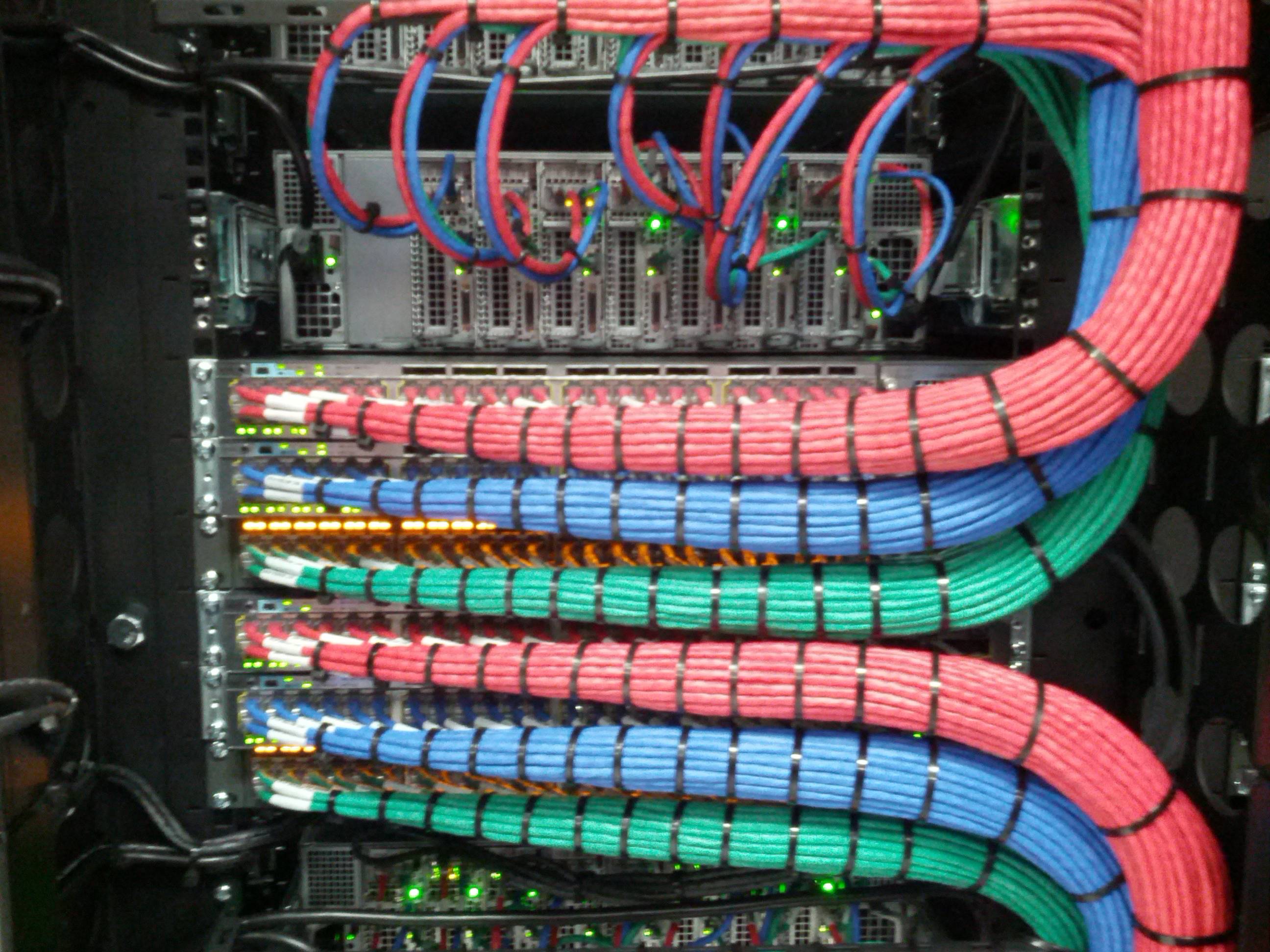
 The most significant trend in IT (information technology) is the greater reliance of organizations on high-performance data communications (datacom)
The most significant trend in IT (information technology) is the greater reliance of organizations on high-performance data communications (datacom) 


 As previously discussed, the transition to IP-based security products and the rapid increase in business applications has resulted in end-users expecting greater video, audio, and data integration. These items require delivery over a standardized
As previously discussed, the transition to IP-based security products and the rapid increase in business applications has resulted in end-users expecting greater video, audio, and data integration. These items require delivery over a standardized 
