
Moving Your Company’s Structured Cabling
 Moving your company also means relocating and setting up its structured cabling at the new location. Minimizing disruption is the key for making the transition smooth, and retaining an experienced cable installation company will make this possible. Their resume should include relocation and new construction because they will need to work with vendors, moving companies, architects, and engineers who will also be involved. This will make the coordination of moving your firm’s IT infrastructure seamless.
Moving your company also means relocating and setting up its structured cabling at the new location. Minimizing disruption is the key for making the transition smooth, and retaining an experienced cable installation company will make this possible. Their resume should include relocation and new construction because they will need to work with vendors, moving companies, architects, and engineers who will also be involved. This will make the coordination of moving your firm’s IT infrastructure seamless.
The move will also involve working with the telecommunication and internet providers to make sure their services are included in the transition plan. The functions they provide are not suspended for an extended period, ensuring swift continuation at the new location.
Services for Relocation
- When hiring a structured cabling company to assist with your move, be sure they can:
- Move the network fast and efficiently.
- Coordinate with Internet and telecommunication providers.
- Ensure safe packing and transport, and unloading of servers, workstations, and printers.
- Transfer e-mail and website services smoothly.
- Set up office network, servers, workstations, and printers at new location.
- Coordinate with outside vendors, including website, Internet, telecommunication, and e-mail services at new location.
- Design cabling diagram for sound network foundation.
- Set up cabling and wiring infrastructure for new location.
Summary of Expertise
Be sure to work with a structured cabling company that is knowledgeable regarding office relocation, network cabling, communications, cable management, computer data cabling, office cabling, and server racks. This depth of knowledge will help minimize unforeseen problems regarding your firm’s structured cabling needs during the relocation. Their experience and expertise will decrease the stress and pressure of moving your IT infrastructure.
Structured Cabling Services
Modern technology features advanced systems that are reliant on sound IT infrastructure that revolves around high-quality cabling and intelligent design. An experienced structured cabling company will understand the needs and requirements of a client and provide the expertise that will minimize costs and maximize infrastructure.
Union Network Cabling
When union work requires a unionized cabling group, call on Union Network Cabling for your commercial Cat5e/6/6a and fiber cabling projects. Specializing in cabling for data, voice, security and even the latest WiFi and LiFi solutions. Phone: (202) 462-4290




 As mentioned previously, modern
As mentioned previously, modern 


 As mentioned in Part 1, modern
As mentioned in Part 1, modern 
 Modern data centers are equipped with devices and networking equipment that connect them. These devices demand increasingly greater bandwidth, and so their fiber or copper
Modern data centers are equipped with devices and networking equipment that connect them. These devices demand increasingly greater bandwidth, and so their fiber or copper 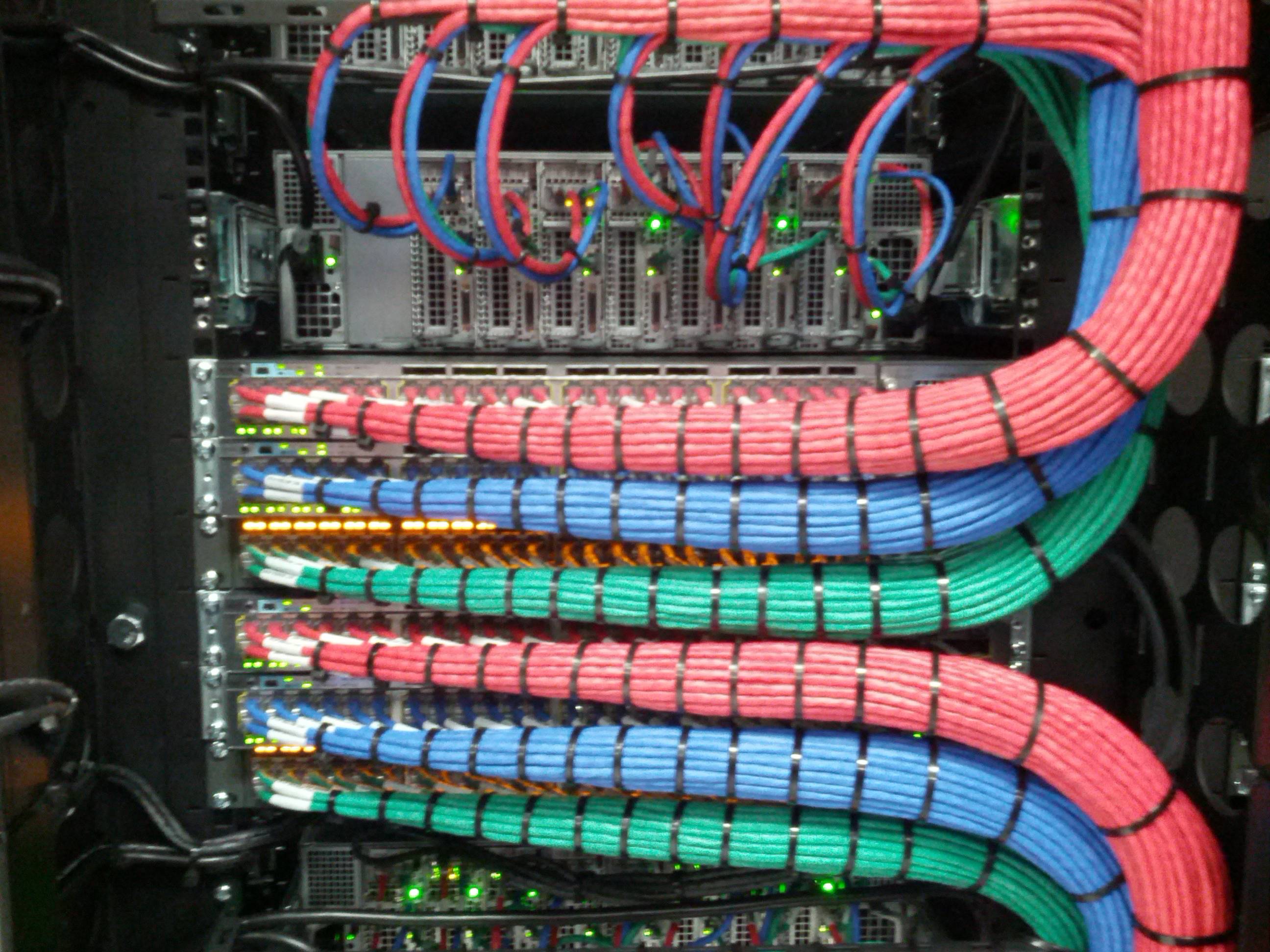
 The structuring of cabling will result in better organization and easier management of the cables. If you are a building manager or business owner, you may already know a bit about
The structuring of cabling will result in better organization and easier management of the cables. If you are a building manager or business owner, you may already know a bit about 
 As mentioned in Part 1, a good
As mentioned in Part 1, a good