
Network Upgrade Planning for Companies – Part 1
 Planning the network upgrade for a company requires careful consideration. Similar to other projects, a need is determined, and then the upgrade process is planned from its start to conclusion. Every sound network upgrade plan will make an analysis determining each aspect of SWOT: Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats. This SWOT analysis will help project managers create a clear plan that defines the tasks required and the order of the workflow.
Planning the network upgrade for a company requires careful consideration. Similar to other projects, a need is determined, and then the upgrade process is planned from its start to conclusion. Every sound network upgrade plan will make an analysis determining each aspect of SWOT: Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats. This SWOT analysis will help project managers create a clear plan that defines the tasks required and the order of the workflow.
Overview
A network constructed as a hodgepodge of devices attached using a combination of protocols and technologies is a sign of substandard initial planning. This lack of forethought results in networks that are prone to downtime, challenging maintenance, and difficult troubleshooting. This poor kind of network is commonly found at small businesses that undergo rapid and unanticipated growth. Big companies also experience this when their networks suddenly expand after a merger with or acquisition of another company. In cases where growth is expected, a company will have a better opportunity to properly plan a network upgrade that is less problematic and provide users adequate service.
Five Phases
Network upgrade planning starts after completion of the initial site survey and report. The plan will be typically divided into five phases as listed below, and each will be then discussed individually.
- Gathering of Requirements
- Selection & Design
- Implementation
- Operation
- Review & Evaluation
1) Gathering of Requirements
Once adequate data has been gathered from visits to the customer and site, the ISP design team will make an evaluation that will determine network requirements and write an analysis report.
2) Selection & Design
After the completion of the analysis report, equipment consisting of devices and cabling will be selected. Several designs will be drafted by the design team, and these will be submitted to other project members for feedback.
This process with allow participants to consider the LAN from a point of view of documentation and assess trade-offs in terms of cost and performance. In addition, design weaknesses will be discovered and solutions will be considered. Moreover, this phase will allow prototyping to determine optimum methodology. Prototypes let designers see how the network will operate before final implementation.
Part 2 will cover the next three phases, Implementation, Operation, and Review & Evaluation.
Union Network Cabling
When union work requires a unionized cabling group, call on Progressive Office Cabling for your commercial Cat5e/6/6a and fiber cabling projects. Specializing in cabling for data, voice, security and even the latest WiFi and LiFi solutions. Phone: (202) 462-4290


 It is inevitable that applications requiring speeds greater than 100 Mbps and 1000 Mbps will increase. The growing use of wireless devices, high resolution images, HD video streaming, surveillance, and multimedia are straining the capacity of
It is inevitable that applications requiring speeds greater than 100 Mbps and 1000 Mbps will increase. The growing use of wireless devices, high resolution images, HD video streaming, surveillance, and multimedia are straining the capacity of 



 After their Milan working group meeting in 2015 regarding
After their Milan working group meeting in 2015 regarding 
 Nowadays offices and homes utilize either a wireless (Wi-Fi) connection or wired
Nowadays offices and homes utilize either a wireless (Wi-Fi) connection or wired 
 The quality of information flow is no better than the medium that carries it. This is the
The quality of information flow is no better than the medium that carries it. This is the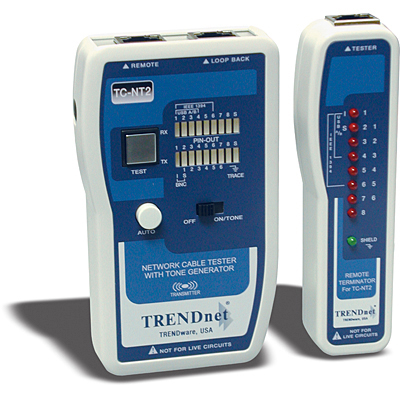 
 Testing always plays a vital role in the process of installing new
Testing always plays a vital role in the process of installing new 
 Data volume has grown extensively. Also, the processing capacity to users continues to get grow. Specialists in
Data volume has grown extensively. Also, the processing capacity to users continues to get grow. Specialists in 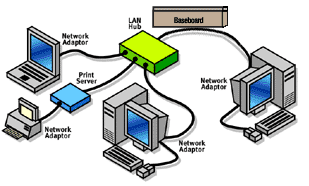
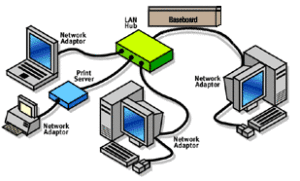 Be sure to purchase the correct components before you install a wired
Be sure to purchase the correct components before you install a wired