
Are you Ready for 2gb Internet?
Your city might be poised for a dramatic increase in Internet speed into your office. Right now, you might have DSL Internet running on Cat5e cable at speeds of up to 25 - 30mb. But 2gb Internet is coming. New high-speed fiber optic networks are being built that will bring 2gb Internet to your office's network. It's coming.
So, are you ready for it?
The answer to that question lies primarily in the cabling that exists in your office. Most offices in the US have Cat5e cabling. Cat5e is not even fully capable of handling 1gb speeds and will likely create speed issues at the desktop as users demand more bandwidth from advanced online and desktop applications. Cat5 cable is even slower. So, you will first need to figure out what kind of cable you have. The best way to do this is to look at the cable. Go to you wall closet or server room and look behind the patch panel. The patch panel looks like this.
And behind the panel is a bundle of cables. These cables have writing on them that describe the type of cable.That might look like this.
You should be able to see printed right on the cable the words "CATEGORY 5" or "CATEGORY 5E". If it says, "CATEGORY 6" or "CATEGORY 6A" than you are fine. Otherwise, you have cable that will not fully support 2gb Internet speeds into your office. Cat6/6A cabling is designed for 2gb and higher throughputs of data.
But getting ready for 2gb Internet is not just about the cable. You need the right cable and you also need the Cat6 compatible connectors, patch panels and a faster switch too. So, now you have a big decision to make.
The Big Decision
What should you do? Recabling an office is a big deal. It's disruptive and it's expensive. But, wait. Is it really such a big expense and does it need to be disruptive? The cost of installing Cat6 cabling in an office is about $175 - $250 per drop. Each computer will need one drop. And you might have a few printers on your network too. So, the cost is about the same as a cheap computer monitor. And the boost in productivity will go on for many years to come.
Will it be disruptive? We can install new cabling in parallel to your existing network at night and on weekends. The switch-over is a weekend job too. Then we finish up by pulling out all of the old cable. That's called demolition. It might get a little dusty. But our team will do it's best to keep things as tidy as possible.
So, are you ready for 1gb Internet? If the service is available and you want a free on-site survey, contact us. We will be happy to come by and look at your office and prepare a Proposal for you at no charge and no obligation. If you aren't sure about the availability of 1gb Internet, contact us and we will find out for you.




 The quality of information flow is no better than the medium that carries it. This is the
The quality of information flow is no better than the medium that carries it. This is the 
 Cabling
Cabling 
 Punch-down
Punch-down 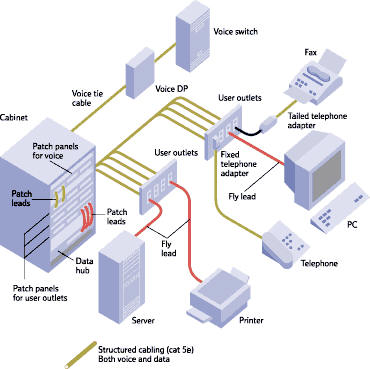
 It is known that
It is known that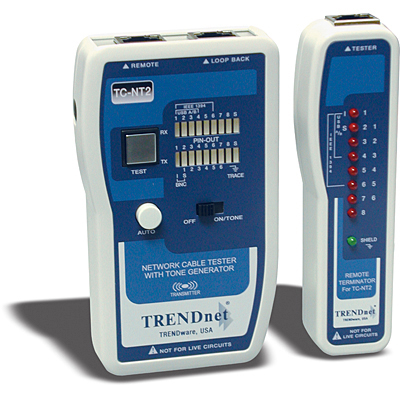 
 Testing always plays a vital role in the process of installing new
Testing always plays a vital role in the process of installing new 
 Data volume has grown extensively. Also, the processing capacity to users continues to get grow. Specialists in
Data volume has grown extensively. Also, the processing capacity to users continues to get grow. Specialists in 
 It is not easy to install
It is not easy to install 
 Be sure to purchase the correct components before you install a wired
Be sure to purchase the correct components before you install a wired