
Advantages of Upgrading to Structured Cabling – Part 1
 If it has been a while since your company has upgraded your network cabling, you and your team may not be achieving your potential. As you know, an organization’s IT network is the very heart of its operations. Lacking a network that is up-to-date, staff members will not be as efficient and productive as possible.
If it has been a while since your company has upgraded your network cabling, you and your team may not be achieving your potential. As you know, an organization’s IT network is the very heart of its operations. Lacking a network that is up-to-date, staff members will not be as efficient and productive as possible.
Updating from Point-to-Point Cabling
The update that yields the most benefits is having your network make the transition from an outdated point-to-point cabling system to a far more effective structured cabling system. As you may know, there are only two ways for transmitting data over network cables. Numerous companies persist on using point-to-point cabling. Unfortunately, it tends to become problematic, especially when a company needs to significantly expand the network’s size and capabilities. Let’s dig deeper to understand the reasons.
Point-to-point cabling directly connects a switch, device, network, a server, or network, to another network component via fiber optic cable. For the last few decades, this wiring method provided an innovative way to swiftly build a network. However, during that period, the majority of networks at IT departments were not large.
Nowadays, as networks expand and speedy transmissions of massive data amounts become routinely expected, the maintenance of outdated point-to-point cabling systems, along with the thousands of cables required for operations, becomes a large burden on a company’s IT resources.
As a result, organizations have transitioned to structured cabling systems. Rather than directly connecting every single network component to another, a structured cabling system directly links storage units and servers to a communication backbone.
Installed in every part of a facility, local cabling panels are linked to the communication backbone with only one cable. This enables users to easily connect their devices to the whole network by connecting a cable to the nearest cabling panel.
Part 2 will discuss the advantages of upgrading to Structured Cabling.
Progressive Office Cabling
Founded in 1986, Progressive Office’s success has been a direct result of years of commitment to seeking solutions on behalf of our clients in the Washington, D.C. and New York City areas. Efficiently working together, Progressive Office teams get cabling installed and operating as fast as possible while minimizing disruption and downtime. Call our toll free number (800) 614-4560 today.


 As discussed in Part 2, there are considerable cost savings from the deployment of zone
As discussed in Part 2, there are considerable cost savings from the deployment of zone 

 As mentioned in Part 1, data center efficiency can be improved by properly planning and implementing structured cabling principles. In addition,
As mentioned in Part 1, data center efficiency can be improved by properly planning and implementing structured cabling principles. In addition, 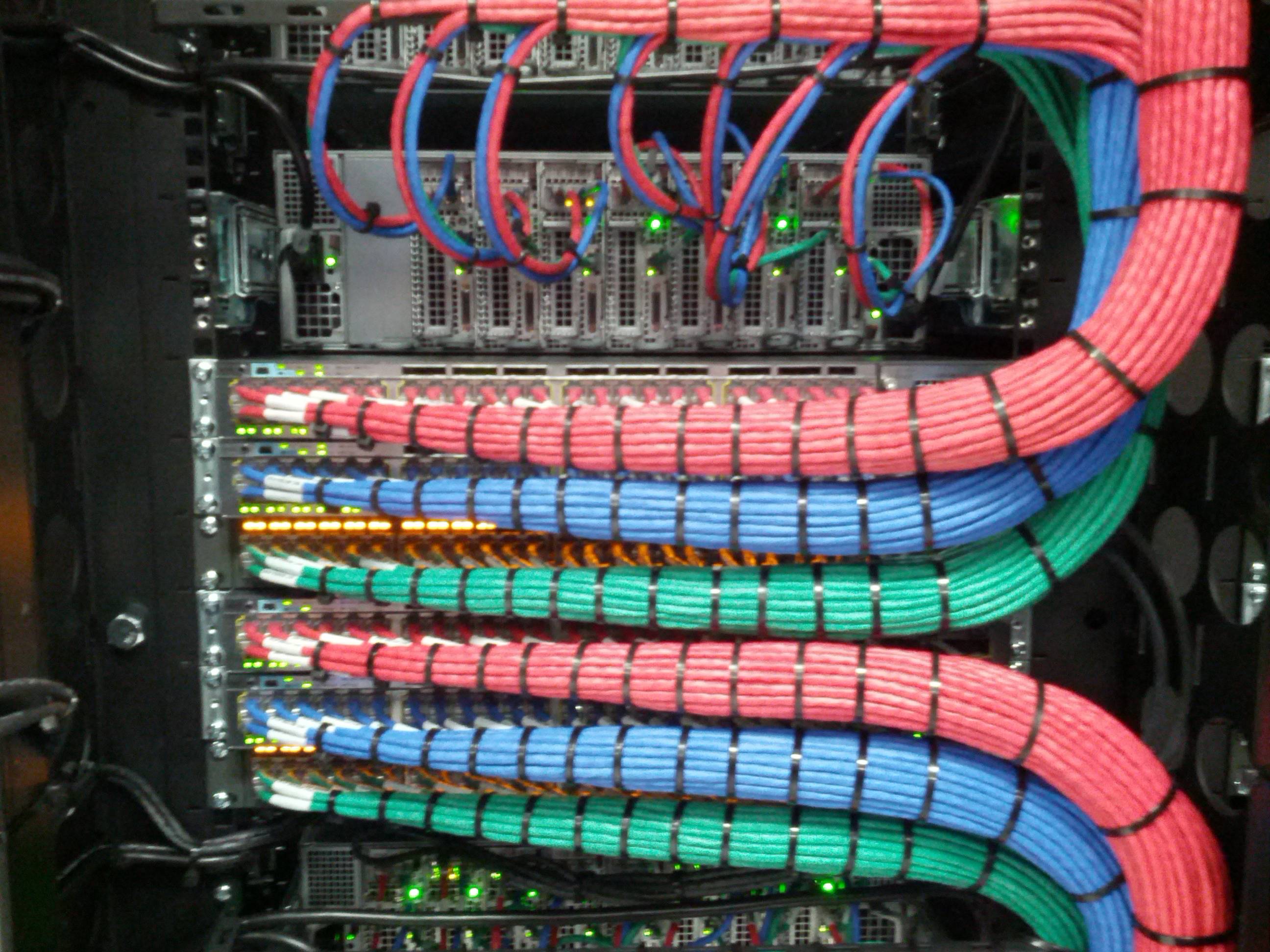


 As discussed in Part 1, the improper I can result in poor network performance, maintenance issues, and concealed expenses. Part 2 will discuss four more
As discussed in Part 1, the improper I can result in poor network performance, maintenance issues, and concealed expenses. Part 2 will discuss four more 

 Your company will need to upgrade because network traffic is rising dramatically due to the rapid increase in the number of devices and videos online. By 2020, the number of devices will approach an estimated 12 billion. The following are reasons why you should contact an expert and experienced structured cabling support team to evaluate and improve your network infrastructure.
Your company will need to upgrade because network traffic is rising dramatically due to the rapid increase in the number of devices and videos online. By 2020, the number of devices will approach an estimated 12 billion. The following are reasons why you should contact an expert and experienced structured cabling support team to evaluate and improve your network infrastructure.
 An infrastructure for enterprise communications,
An infrastructure for enterprise communications,