
Introduction to Network Cabling – Part 2
 As mentioned in Part 1, cabling utilized for network infrastructure is a crucial aspect of networking, growing in importance as new technologies are introduced. Although wireless technology has made great advancements, existing computer networks are still using cables for transferring data. Part 2 will cover Fiber Optics, USB Cables, and Crossover Cables.
As mentioned in Part 1, cabling utilized for network infrastructure is a crucial aspect of networking, growing in importance as new technologies are introduced. Although wireless technology has made great advancements, existing computer networks are still using cables for transferring data. Part 2 will cover Fiber Optics, USB Cables, and Crossover Cables.
Fiber Optics
In contrast to older wiring, fiber optic network cables utilize strands of glass and pulses of light to carry data. Although composed of glass, these cables can be bent and have proven their utility in wide area network (WAN) installations in office buildings, especially when long distance runs are necessary and a high volume of communication traffic is typical.
The two main fiber optic cable standards are single mode, the 100BaseBX standard, and multimode, the 100BaseSX standard. Due to single mode's higher bandwidth capacity, it is typically used by long distance telecommunications networks. On the other hand, local networks commonly utilize multimode because of its lower cost.
USB Cables
USB (Universal Serial Bus) cables, which feature twisted pair wiring, are typically used to connect a peripheral device, such as a mouse, to a computer. Dongles or special network adapters also permit the indirect connection of an Ethernet cable to a USB port.
Serial & Parallel Cables
As numerous PCs during the 1980s and early 1990s did not have Ethernet capability, along with the fact USB did not yet exist, now obsolete serial and parallel interfaces were occasionally utilized for networking PCs together. As an example, null modem cables connected the serial ports of two PCs, allowing 0.115 to 0.45 Mbps data transfer.
Crossover Cables
A null modem cable belongs in the category of crossover cables because it joins two network devices of the identical type, like two network switches or two PCs. Ethernet crossover cable usage was most commonly found in home networks years ago when two PCs were directly connected. Currently the majority of home networks are equipped with routers featuring crossover capability, making crossover cables unnecessary.
Union Network Cabling
When union work requires a unionized cabling group, call on Union Network Cabling for your commercial Cat5e/6/6a and fiber cabling projects. Specializing in cabling for data, voice, security and even the latest WiFi and LiFi solutions. Phone: (202) 462-4290





 Modern data centers are equipped with devices and networking equipment that connect them. These devices demand increasingly greater bandwidth, and so their fiber or copper
Modern data centers are equipped with devices and networking equipment that connect them. These devices demand increasingly greater bandwidth, and so their fiber or copper 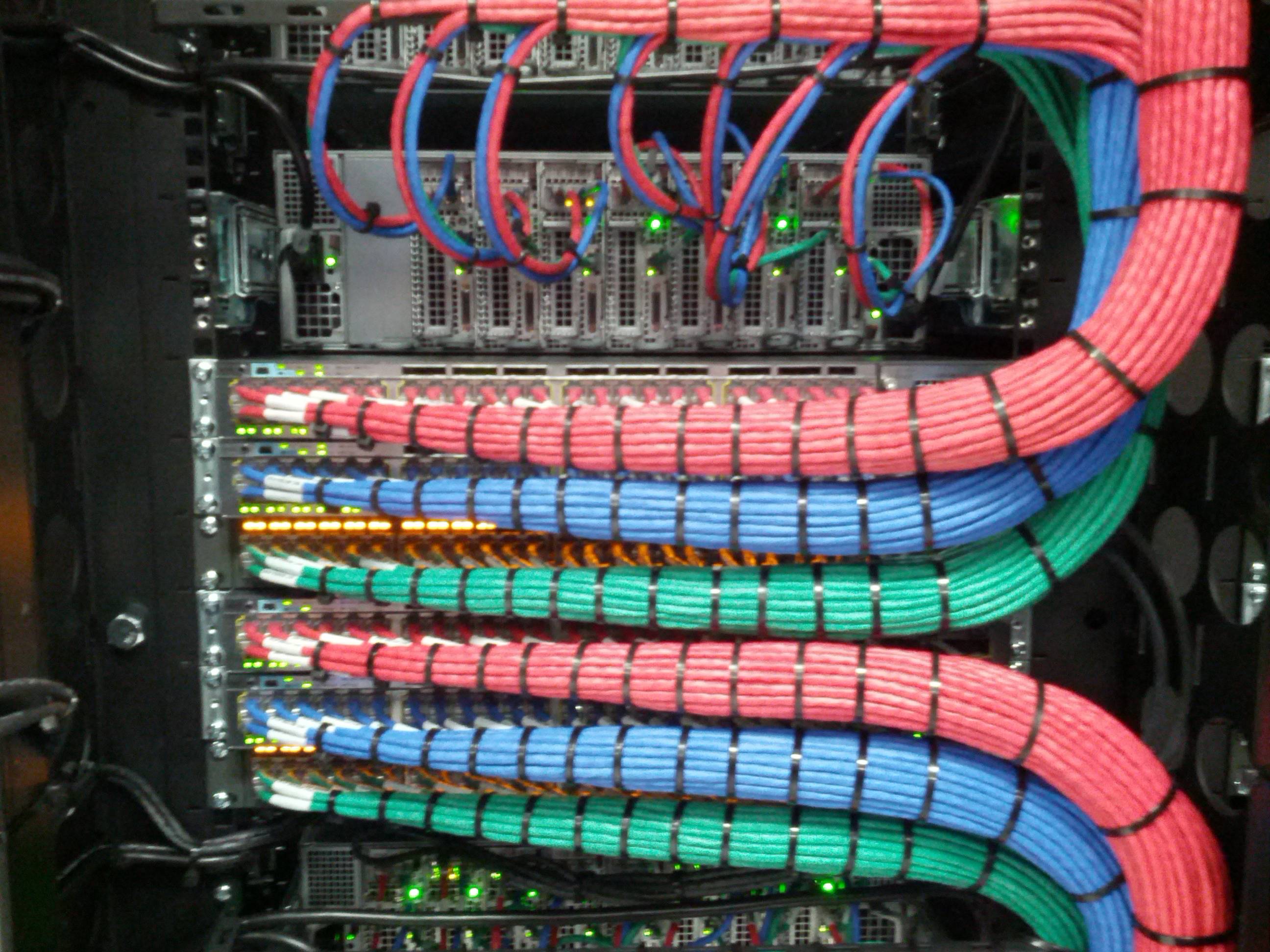
 The structuring of cabling will result in better organization and easier management of the cables. If you are a building manager or business owner, you may already know a bit about
The structuring of cabling will result in better organization and easier management of the cables. If you are a building manager or business owner, you may already know a bit about 
 It is inevitable that applications requiring speeds greater than 100 Mbps and 1000 Mbps will increase. The growing use of wireless devices, high resolution images, HD video streaming, surveillance, and multimedia are straining the capacity of
It is inevitable that applications requiring speeds greater than 100 Mbps and 1000 Mbps will increase. The growing use of wireless devices, high resolution images, HD video streaming, surveillance, and multimedia are straining the capacity of 
 Nowadays offices and homes utilize either a wireless (Wi-Fi) connection or wired
Nowadays offices and homes utilize either a wireless (Wi-Fi) connection or wired 
 Cabling
Cabling 
 Punch-down
Punch-down